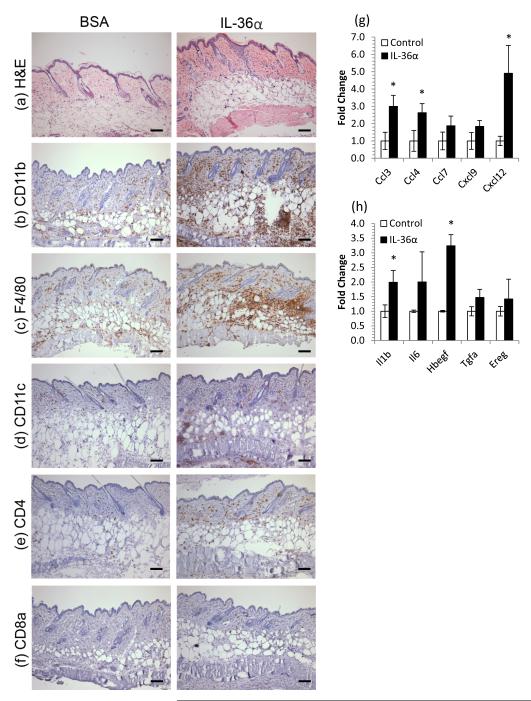
Figure 2. IL-36 induces myeloid cell infiltration of skin concomitant with chemokine and growth factor induction.
5μg rmIL-36α or BSA was injected intradermally into CD1 mice every other day for 10 days. Back skin was harvested, snap frozen, processed for RNA and histochemistry. IL-36α treatment lead to acanthosis and an increase in eosinophilic dermal collagen (a) and striking infiltration of granulocytes (CD11b, b), macrophages (F4/80, c), dendritic cells (CD11c, d) CD4+ cells (e) but not CD8+ cells (f). These changes were accompanied by increases in chemokines (g) and cytokines/growth factors (h). Mean ± SEM (n=4 mice). Statistical significance indicated by * p<0.05 (2-tailed t-test). Scale bar = 100μm.