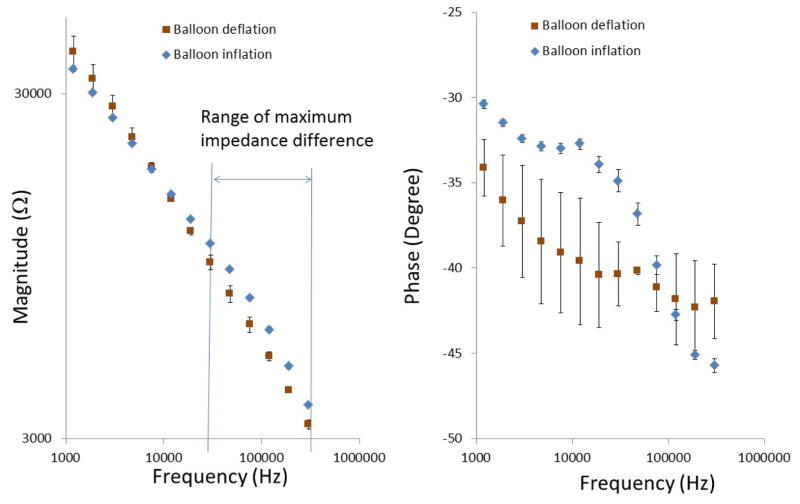
Fig. 6.
In-vivo EIS acquisition in the rabbit carotid arteries. Balloon-inflatable EIS sensor packaged onto an in-house built balloon catheter. Catheter was deployed through right carotid artery cut-down and the sensor was made endoluminal contact under the fluoroscopic guidance. Inflation of balloon resulted in a significant increase in the frequency-dependent impedance magnitude from 10 kHz to 300kHz, along with the distinct phase characteristics.