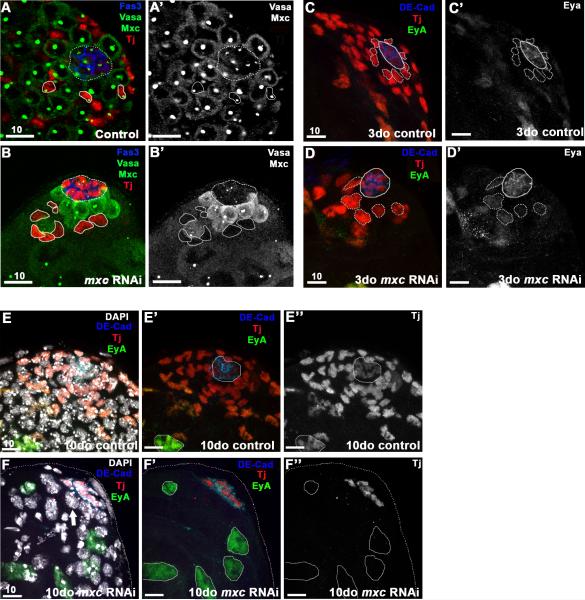
Figure 2. A-D’ : Mxc is required autonomously for maintenance of early cyst cells.
RNAi-mediated knock-down of mxc (RNAi induced for 7d) in early cyst cells (Tj+, red) using the c587GAL4 driver results in a significant reduction in cyst cells at the testis tip, including CySCs (B), when compared to controls (A). Loss of Mxc staining in cyst cells (circled, B-B’ compared to A-A’) confirmed efficiency of RNAi-mediated knockdown. Germ cells (Vasa, green), Mxc (HLB, green), and hub (Fas3, blue; dashed circle). C-D The nuclei of Tj+ cells adjacent to the hub (CySCs, dotted line) are significantly larger 3 days after induction of mxcRNAi (D, D’) when compared to controls (C, C’) and express higher levels of the late cyst cell marker Eyes absent (Eya, green), indicating precocious differentiation. Early cyst cells (Tj+, red), hub (DE-cad+, blue), late cyst cells (Eya+, green). E-F” : Ten days after induction of mxcRNAi, late cyst cells (EyA+/Tj-, green) replace early cyst cells (Tj+, red) at the apical tip (F-F”). DAPI staining in F reveals the presence of germ cells (Tj-, EyA-) at the tip of the testis, adjacent to the hub (thick arrow), similar to B. Scale bars indicated in μM.