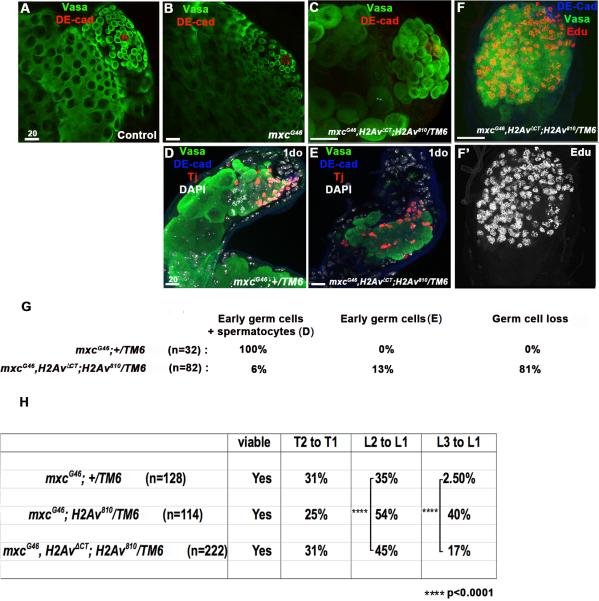
Figure 5. Mutations in H2Av enhance the onset of mxc germline phenotypes and ectopic sex combs.
A-D. Male gonads from (A) wild-type and (B) mxcG46 3rd instar larvae appear wild-type, while the mxc mutant phenotype is detected at this stage in mxcG46,H2AvΔCT;H2Av810/TM6b (C) male larvae. Germ cells (Vasa+, green); hub (DE-cad+, red). (D, G) Testes from 1-day old mxc G46 adults, exhibit a combination of early germ cells and large germ cells that have initiated differentiaiton prematurely. Germ cells (Vasa+, green); hub (DE-cad+, blue); cyst cells (Tj+, red). (E, F, G) Testes from 1-day old mxcG46,H2AvΔCT; H2Av810/TM6b flies accumulate spermatogonia that appear to be stalled in S-phase, as indicated by EdU incorporation. (H) The L2 to L1 and L3 to L1 transformations are enhanced in mxcG46 ;H2Av810/TMb and mxcG46, H2AvΔCT;H2Av810/TM6b flies.