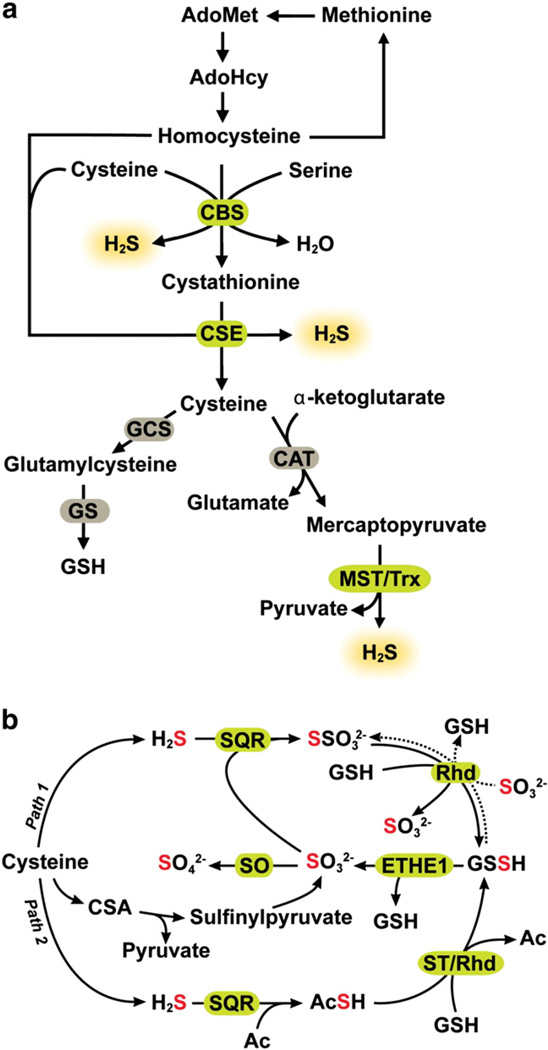
Fig. 2.
Pathways for sulfide biogenesis and clearance. (a) H2S is synthesized from the amino acids, cysteine and homocysteine via the transsulfuration pathway enzymes, CBS and CSE and by the action of CAT, MST and thioredoxin (Trx) as described in the text. (b) Sulfide oxidation occurs in the mitochondrion. While the first reaction is catalyzed by SQR, the subsequent steps in the pathway remain to be defined. In “path 1” sulfite is shown as the acceptor of sulfane sulfur from SQR while in “path 2”, the acceptor (Ac) is not known and is an intermediate carrier of the sulfane sulfur between SQR and glutathione. The following new abbreviations are used in the figure: Ac (acceptor), GCS (γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase), GS (glutathione synthetase), Rhd (rhodanese), ST (sulfurtransferase).