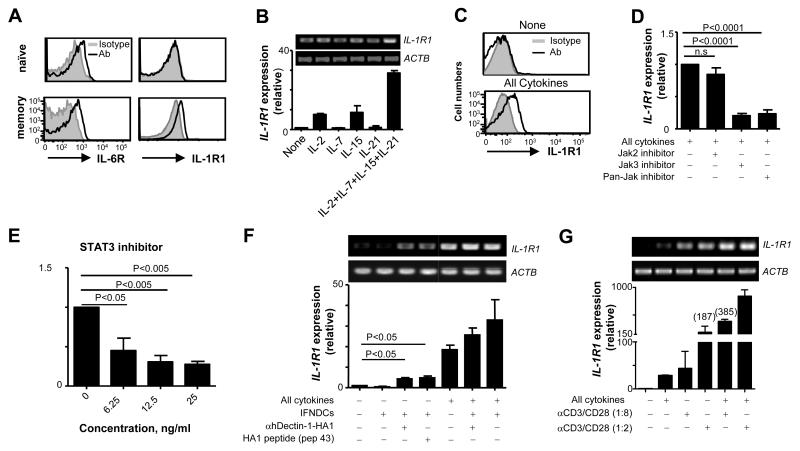
FIGURE 5.
Naïve CD4+ T cells do not express IL-1R1 that is inducible by synergistic actions of signals from TCRs and common-γ chain receptors. (A) IL-1R1 and IL-6R expression on naïve and memory CD4+ T cells in the peripheral blood. CD4+ T cells from 6 healthy donors showed similar results. (B) Real-time (lower panel) and conventional (upper panel) RT-PCR analysis of IL-1R1 expression in naïve CD4+ T cells treated for 18h with indicated cytokines. (C) Surface IL-1R1 expression on naïve CD4+ T cells treated for 36h with the combination of the cytokines in (B). (D and E) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of IL-1R1 expression in naïve CD4+ T cells treated with the combination of the cytokines in (B) in the presence or absence of indicated inhibitors. Data are pooled from three independent experiments. P values were acquired by the Student’s t-test. (F and G) Real-time (lower panel) and conventional (upper panel) RT-PCR analysis of IL-1R1 expression in naïve CD4+ T cells co-cultured overnight with IFNDCs alone, IFNDCs loaded with HA1 peptide (Pep 43, 1 μM), or IFNDCs loaded with 1 μg/ml anti-hDectin-1-HA1 in the presence or absence of the combination of common γ-chain cytokines (F) or different amounts of anti-CD3/CD28-coated microbeads (G). (F) Error bars indicate mean±SD of duplicate assay of two independent experiments. In (B), (C), and (G), Error bars indicate mean±SD of triplicate assay and three independent experiments showed similar results. P values were acquired by the Student’s t-test.