Figure 3. Tissue-engineered models of Ewing’s sarcoma (TE-ES).
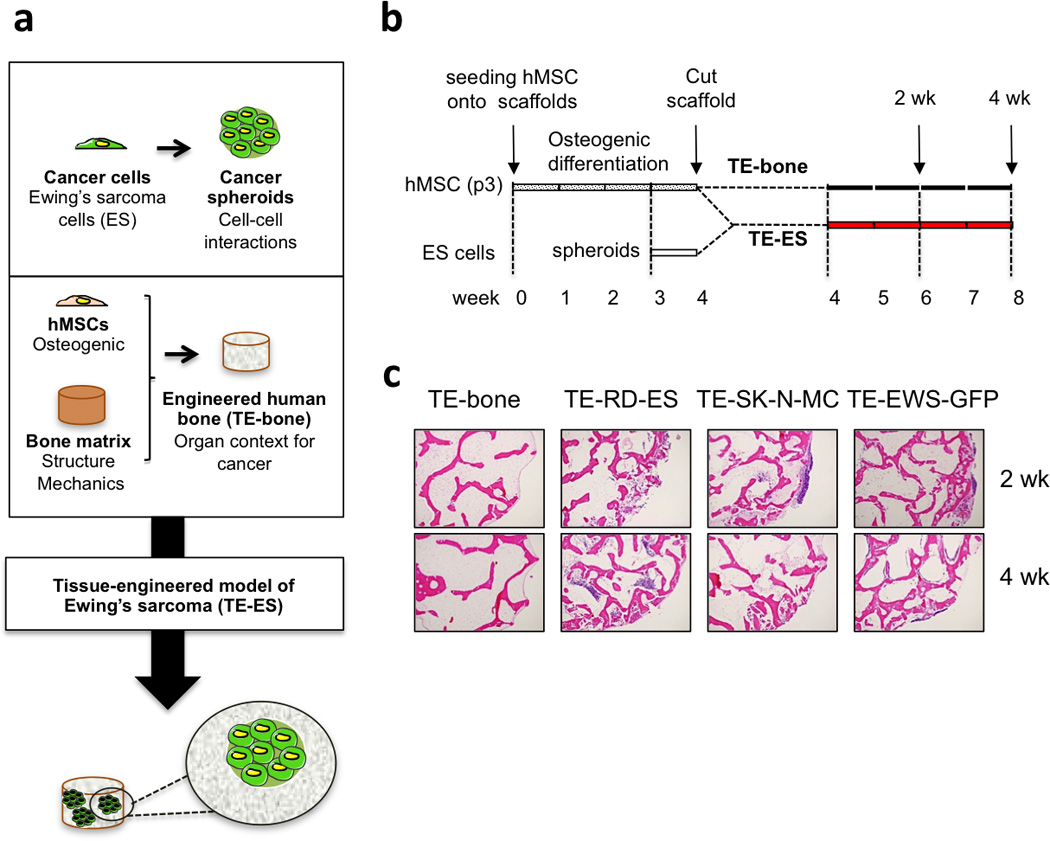
(a) Methodology used to develop tissue-engineered models of Ewing’s sarcoma tumors. (b) TE-ES generation. Fully decellularized bone scaffolds (4 mm diameter × 4 mm high plugs) were seeded with hMSCs (p3). After 4 weeks of culture in osteogenic differentiation medium, bone constructs were bisected. One half was seeded with Ewing’s sarcoma spheroids (3 per construct); the other half was used as control (TE-bone). Both TE-ES and TE-bone were cultured for 2 or 4 weeks in ES medium. (c) Hematoxylin and Eosin images of TE-bone controls and TE-ES models (TE-RD-ES, TE-SK-N-MC, TE-EW-GFP) at week 2 and 4 after introducing tumor spheroids.
