Fig. 4.
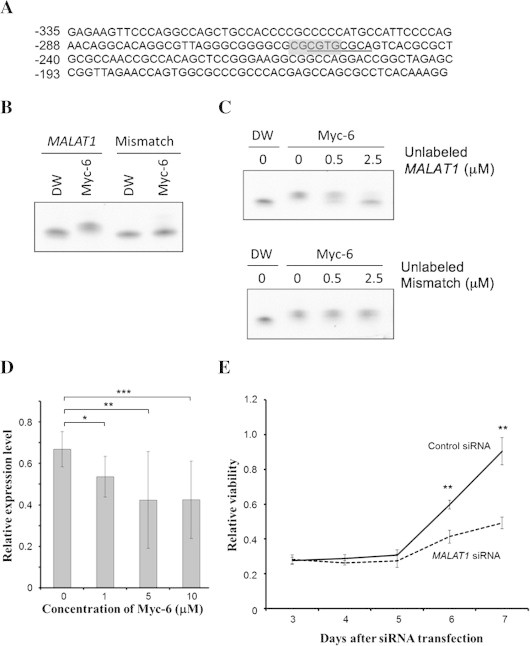
MALAT1 is one of possible target genes of Myc-6. (A) Sequence of 5′-upstream region of human MALAT1 gene. The positions relative to the first nucleotide of MALAT1 exon 1 (+1) are indicated. The putative Myc-6-target sequence is underlined, and E-box-like sequence is highlighted in gray. (B and C) Gel retardation assay. FITC-labeled specific (MALAT1) or non-specific (Mismatch) oligonucleotide (1 μM) was incubated with water or Myc-6 (5 μM) for 1 h at 37 °C. The reaction mixtures were separated by 4–20% gradient polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and then analyzed by LAS4000 (FUJIFILM) (B). FITC-labeled specific oligonucleotide (0.5 μM) was incubated with Myc-6 (0.5 μM) in the presence or absence of the indicated amounts of unlabeled specific (upper) or non-specific (lower) oligonucleotides. The reaction mixtures were analyzed as in (B) (C). (D) Myc-6-mediated down-regulation of MALAT1. MG63 cells were treated with or without the indicated concentrations of Myc-6. Twenty-four hours after treatment, the expression level of MALAT1 was analyzed by real-time PCR. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. The columns represent means ± SD. (E) Knockdown of MALAT1 suppresses MG63 cell growth. MG63 cells were transfected with control siRNA or with siRNA against MALAT1. The cell viability was assessed by WST-8 assay. ∗∗p < 0.001.
