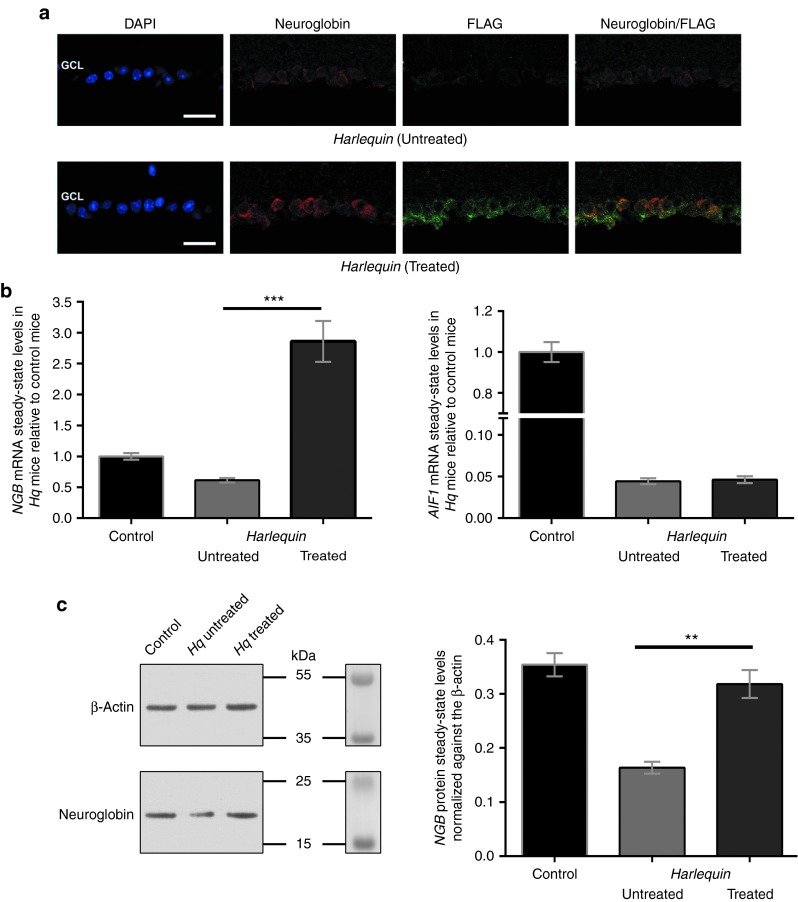
Figure 4.
Neuroglobin (NGB) transgene expression in Harlequin (Hq)-treated eyes. (a) AAV2/2-NGB transduction efficiency was further evaluated by immunostaining for a FLAG antibody which recognized the NGB protein synthesized from the vector. A strong labeling for FLAG (green) was restricted to the GCL of AAV2/2-NGB treated retinas; additionally, a high extent of fluorescent signal overlapping was observed in all the cells between antibodies against NGB (red) and FLAG. Scale bar is 50 μm for both panels. (b) RT-qPCR assays were performed with total RNAs extracted from 18 control retinas and 15 pairs of retinas isolated from Hq mice in which one eye was subjected to intravitreal injection of AAV2/2-NGB. Histograms show the steady-state levels of NGB mRNA and AIF1 mRNAs relative to the value assessed in RNAs from control retinas. Primers used are shown in Supplementary Table S2. (c) Representative western blots from retinas of 7-month-old Hq in which eyes were subjected to AAV2/2-NGB treatment reveals an increase of NGB signal relative to Hq-untreated retinas. The membrane before incubation with the antibodies and the prestained markers sharing similar electrophoretic properties to proteins evaluated were shown. Histogram (right panel) shows the relative amount of the NGB protein in retinas from untreated Hq (n = 8), treated Hq (n = 6), and age-matched controls (n = 12). The densities of NGB signals were normalized to β-actin signals.