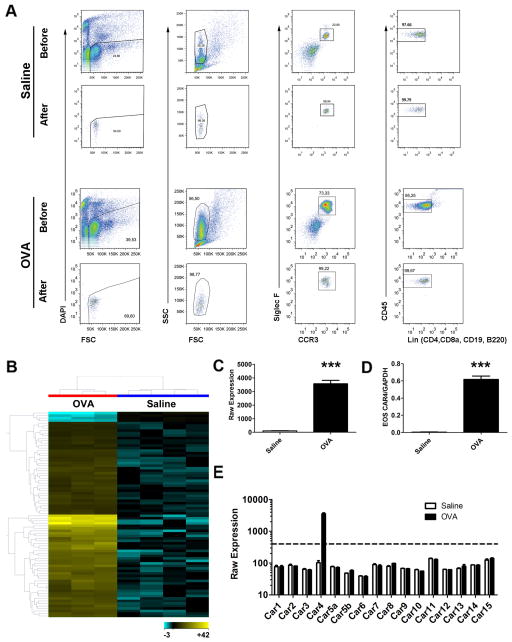
Figure 1. Unique transcriptome of activated lung eosinophils and Car4 validation.
A, After allergen (OVA, n = 3) and saline (n = 4) challenge, lung tissue eosinophils were isolated by FACS following enzymatic digestion to harvest eosinophil RNA. Live eosinophil events were identified as DAPI−CCR3+Siglec-F+CD45+CD4−CD8a−CD19−B220−SSChigh with a purity > 95–99% confirmed by sample back-run (Saline and OVA, before and after FACS sorting graphs shown). B, Eosinophil mRNA was subjected to genome-wide mRNA microarray (Affymetrix mouse ST 1.0 chip), resulting in 78 upregulated and 4 downregulated genes following activation (upper 80th percentile expression, fold change > 2.0, FDR-corrected p < 0.05). On the basis of these significant genes, a heat-map was established double-clustered on entity (gene, y axis) and condition (treatment, x axis), with yellow indicating high expression and blue indicating low expression (Table S1). C, The Affymetrix raw expression value of Car4 probes, saline (n = 4) vs. OVA (n = 3)-challenged eosinophils. D, The microarray finding of Car4 overexpression was validated by quantitative PCR (with Gapdh normalization). E, The Affymetrix raw expression values of all 16 Car family members embedded on the microarray were displayed, saline vs. OVA challenged, with a value of 400 units deemed as significantly expressed (*** p < 0.001, all data presented as mean ± SEM). EOS, eosinophils.