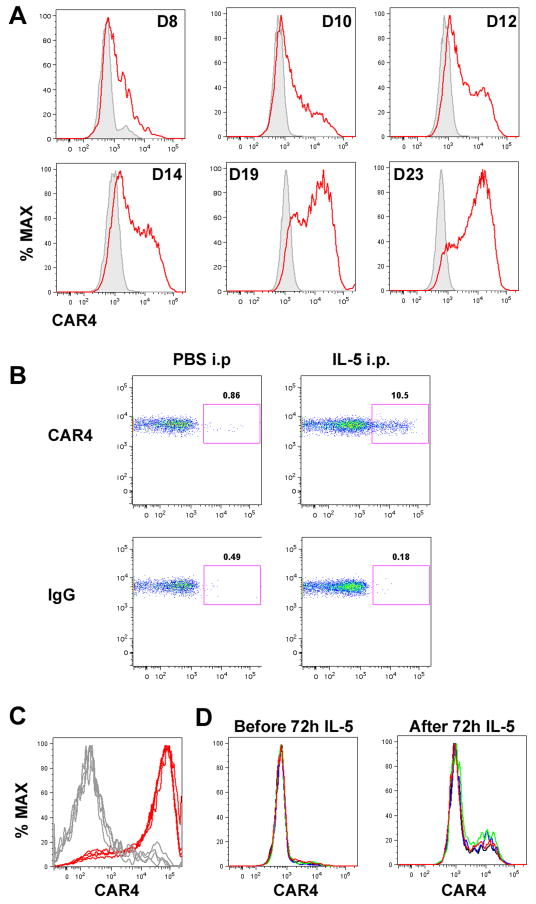
Figure 4. Role of IL-5 for CAR4 induction.
A, Bone marrow–derived eosinophils CAR4 expression following IL-5 induction (10 ng/mL). Gated eosinophil CAR4+ expression histograms (red) (in reference to IgG staining (grey)) on cultured eosinophils were plotted on different days. B, IL-5 (1 μg) or saline (PBS) was administrated into the peritoneal cavity of naïve mice. After 24 hours, peritoneal eosinophil CAR4 expression was assessed by FACS, and CAR4 expression on gated eosinophils (CD45+SSChighSiglec-F+CD11b+GR-1+CD11c− ) is shown on the double-plot (CCR3-CAR4) controlled by IgG staining. C, Histograms of bronchoalveolar (BALF) eosinophil CAR4 expression from allergen-challenged Il5+/+ (red) and Il5−/− (grey) mice (n = 4 mice per group, superimposed). D, In the same experiment, the total BALF cells from Il5−/− asthmatic mice, largely consisting of CAR4− eosinophils, were cultured in IL-5-containing media (20 ng/mL) for 72 hours. Surface CAR4 expression was compared before and after the IL-5 treatment (n = 4 mice per group, superimposed, 2.8 ± 0.2% vs. 15.5 ± 3.5% CAR4+, mean ± SD).