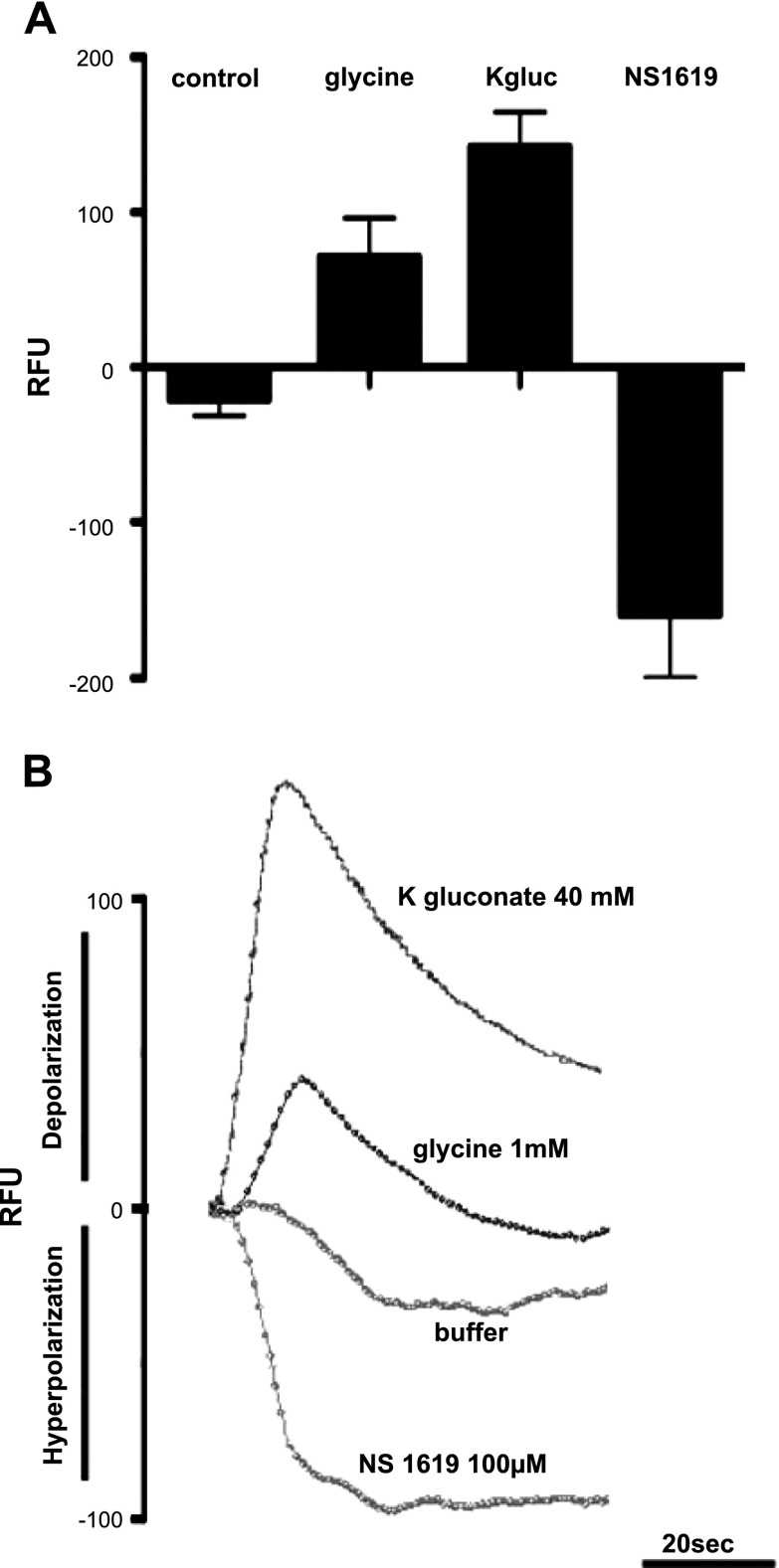
Figure 6.
FLIPR dye assessment of depolarization and hyperpolarization stimulation of airway smooth muscle in response to NS1619, K-gluconate and glycine. A) Graphical representation of FLIPR potentiometric dye fluorescence emissions (RFU) after cultured airway smooth muscle cells were treated with either buffer (control), 1 mM glycine, 40 mM K-gluconate, or 100 μM NS1619 (n=6–12). Mean mean ± se fluorescence change for 1 mM glycine is 71 ± 25 RFU; for K-gluconate, 142 ± 22 RFU. B) Representative tracing of real-time FLIPR potentiometric dye fluorescence emissions after cultured airway smooth muscle cells were treated with either buffer, 1 mM glycine, 40 mM K-gluconate, or 100 μM NS1619. Tracings display directionality of fluorescence change in relation to depolarization (upward deflection: glycine K-gluconate) and hyperpolarization (downward deflection: NS1619).