FIGURE 1.
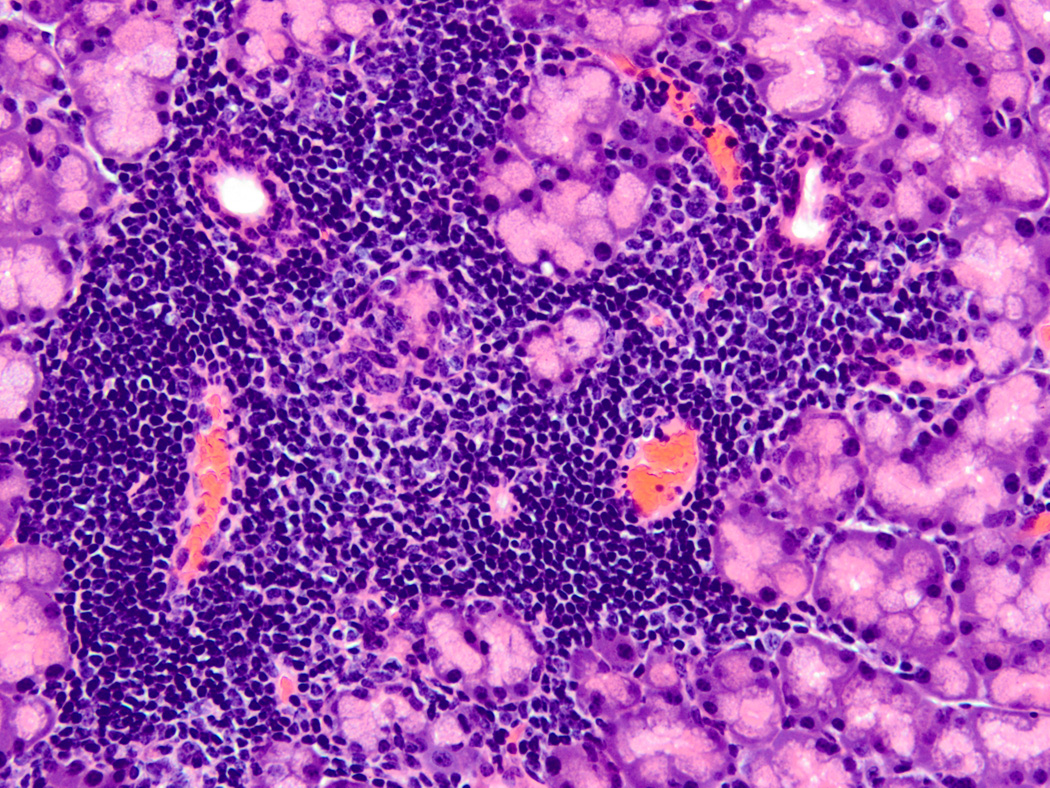
Typical SS focal lymphocytic infiltrate. Hematoxylin and eosin stained section from a formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded lacrimal gland of a 10 week old male nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse (original magnification 200X). This image depicts a typical focal lymphocytic infiltrate in the periductal and perivascular distribution surrounded by normal acinar tissue. The ducts are present in the upper left and right of the focus, and the blood vessels are in the lower left and right. Similar focal infiltrates are also found in salivary glands of NOD and related mice as well as salivary and lacrimal glands of human SS patients. A focus is defined as a group of at least 50 mononuclear cells, and the focus score (FS) is defined by the number of these lymphocyte-dominant foci per 4 mm2 of tissue section.
