FIG 4 .
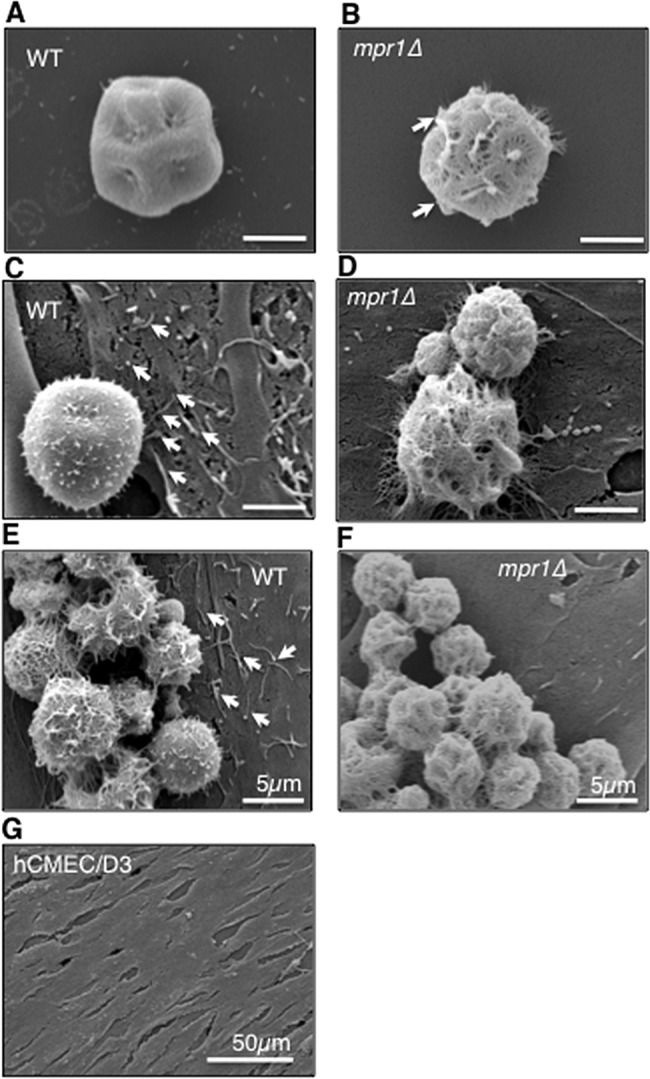
Mpr1 alters the extracellular environment of the fungus-endothelium interface. Scanning electron micrographs of cryptococcal cells from H99 and mpr1Δ strains reveal physical differences at the brain endothelium-fungus interface. In the absence (A and B) or presence (C to F) of hCMED/D3 cells (brain endothelial cells), the mpr1Δ null cells displayed a more porous surface than H99 cells (indicated by arrows). (C and E) Exposure of hCMED/D3 cells to H99 revealed extensive microvillus-like structures that appeared to be less abundant upon coincubation with mpr1Δ cells (D and F) (indicated by arrows). The microvillus-like protrusions were not observed on the surface of hCMED/D3 in the absence of C. neoformans (G) (scale bar = 2 µm unless noted differently in the figure).
