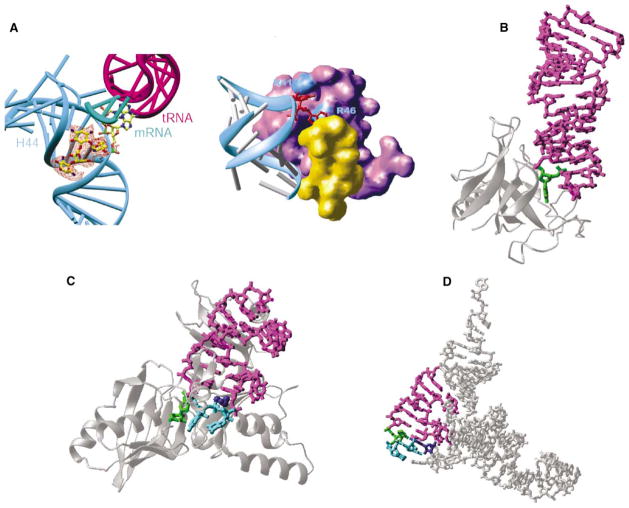
Figure. Examples of RNA Base Flipping.
(A) 30S ribosomal subunit: flipped-out A1492 and A1493 from helix 44 (in cyan) of 16S RNA by binding of paromomycin (left, seen in the orange difference density) and initiation factor IF1 (right, in purple). The protein S12 is in yellow.
(B) Restrictocin-RNA complex (Protein Data Bank code 1JBR). The RNA is presented as a magenta stick model, with the flipped nucleotide in green. The enzyme is represented as silver ribbons.
(C) TruB-tRNA complex (Protein Data Bank code 1K8W). The flipped nucleotides are in green (U55) and cyan (C56 and G57). The amino acid His43 in dark blue stacks with U54:A58 pair.
(D) Stick model of yeast tRNAPhe (Protein Data Bank code 1EHZ), with the stem loop in magenta, U55 in green, C56 and G57 in cyan, and G18 of D loop in dark blue.