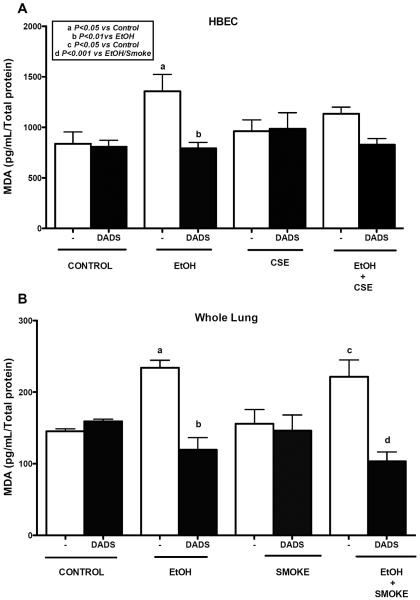
Fig. 3. Effect of ethanol and cigarette smoke on MDA levels in HBECs and C57BL/6 mice whole lung tissue homogenate.
Lysate of human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) were pretreated for 1 hr with diallyl disulfide (DADS; 10 μM) and further exposed to ethanol (EtOH; 80 mM), cigarette smoke extract (CSE; 5%) and co-exposure condition for 6h and crude homogenates of mouse lung tissue were assayed for malondialdehyde (MDA) levels using a sandwich ELISA. Ethanol alone significantly increased MDA levels. Exposure to ethanol and cigarette smoke significantly increased MDA levels in tissue homogenate, which was reduced significantly by DADS supplement. Values represent mean ± S.E.M. of n=4 mice and n=3 independent experiments for HBECs.