Fig. 5. Proposed model of M1dG adduct formation.
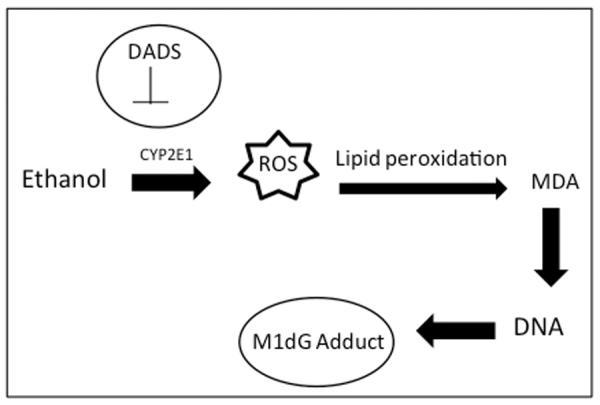
CYP2E1 mediated metabolism of alcohol leads to generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS enhances lipid peroxidation leading to the generation of malondialdehyde (MDA), which can adduct to the guanosine base of DNA to form a M1dG adduct. Inhibition of CYP2E1 by diallyl disulfide (DADS) leads to reduction in both MDA levels and M1dG adduct formation.
