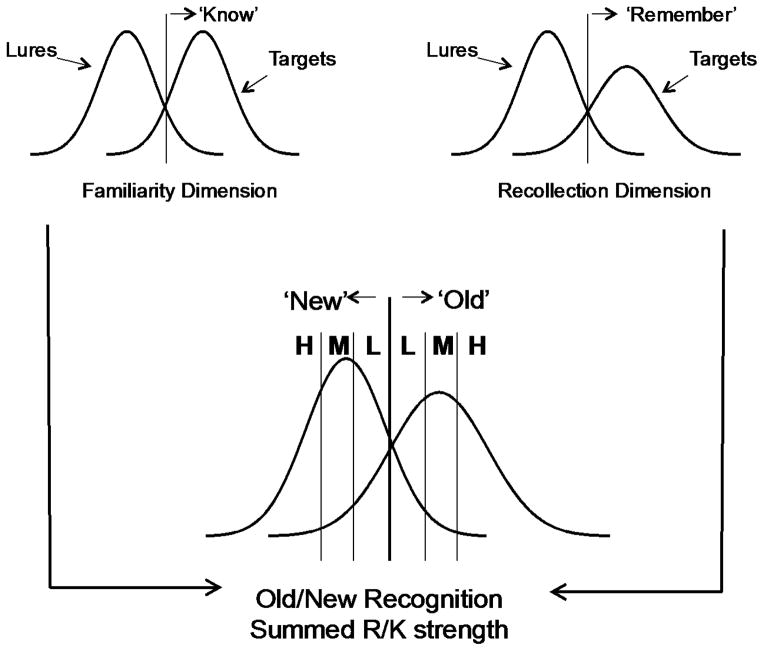
Figure 3.
Continuous dual process model (CDP). Under this model recollection and familiarity are separate, orthogonal dimensions where both processes follow a continuous signal detection model. Familiarity assumes an equal variance model whereas recollection assumes an unequal variance model. Observers make old/new recognition assessments by evaluating a hybrid signal, which is the sum of both independent processes, and determining whether this summed signal surpasses and old/new decision criterion. Confidence ratings follow a distance to criterion account using the summed recollection/familiarity signal. For items reported as old, observers assess for evidence of recollection and then for familiarity in order to determine if an item is Remembered vs. Known.