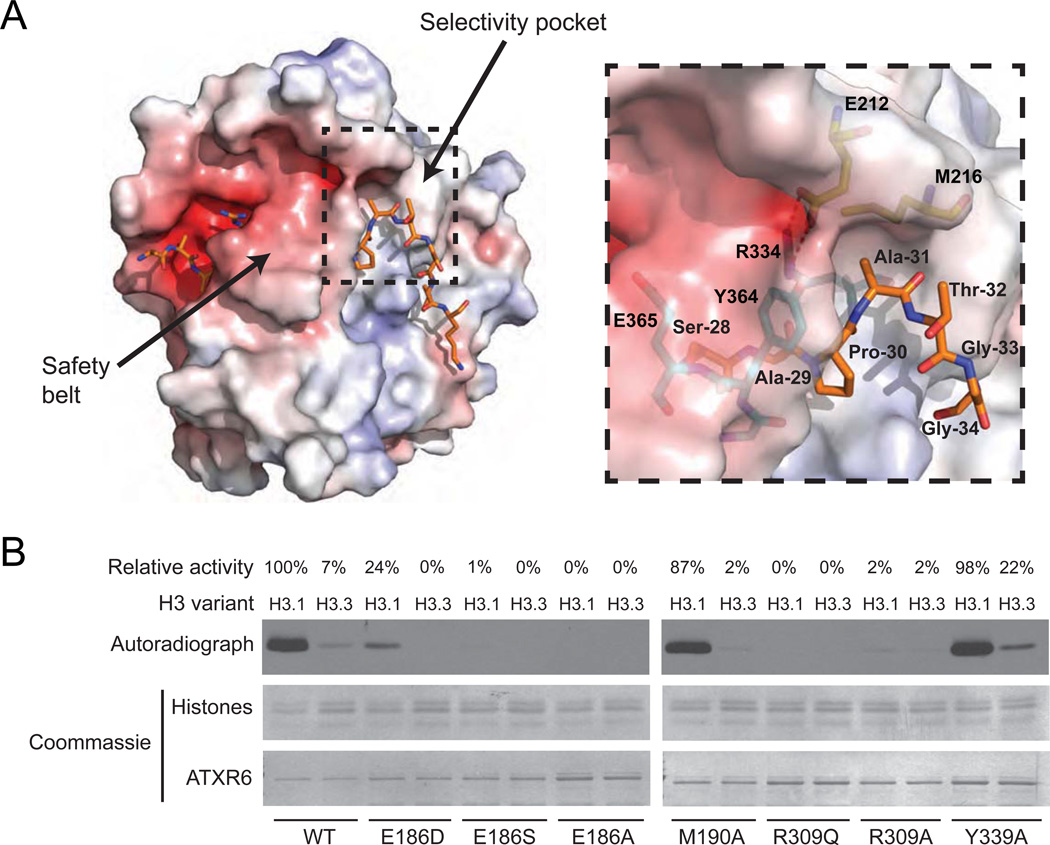
Figure 3. The selectivity pocket and safety belt of ATXR5/6-type H3K27 methyltransferases are responsible for histone H3.1 preference over histone H3.3.
A. The structure of the ATXR5-H3.1-SAH complex in electrostatic potential surface representation with the selectivity pocket and safety belt highlighted. Positive and negative potentials are in blue and red, respectively. Inlet figure shows a zoomed view of the residues forming the surface of the selectivity pocket (three-letter code refers to histone H3.1 residues; one-letter code refers to RcATXR5). Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed red lines. B. In vitro HKM assay using recombinant chromatin containing plant histone H3.1 or H3.3 as substrates and wild-type or point mutants of ATXR6 from A. thaliana. The enzymatic activity indicated for each reaction is relative to the activity of ATXR6 (WT) on H3.1 nucleosomes.