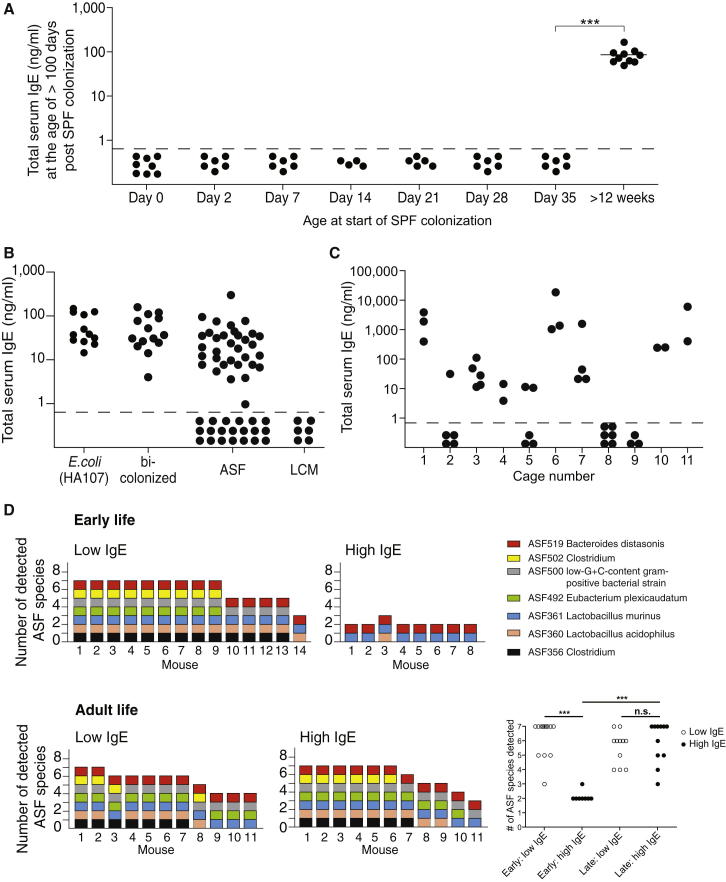
Figure 6.
Increased Intestinal Bacterial Diversity in Neonates Abrogates Hyper-IgE
(A) Germ-free C57BL/6 mice were colonized with an SPF flora by cohousing with an SPF sentinel at the indicated age after birth (n = 4–10 mice per group). Total serum IgE levels were measured >100 days after SPF colonization.
(B) Total serum IgE levels were measured in adult germ-free C57BL/6 mice that were orally administered three to six gavages of 2 × 109−1010 CFU of the auxotrophic E.coli strain HA107 before weaning (n = 12), bicolonized from birth with ASF519 (P. distasonis) and ASF361 (L. murinus) (n = 14), ASF colonized from birth (n = 52), or colonized from birth with a low-complexity microbiota (LCM) consisting of approximately 40 species (n = 6).
(C) Total serum IgE levels were measured in adult (>6 weeks old) ASF mice raised in a flexible film isolator within individual cages as indicated (n = 2–6 per cage).
(D) DNA was isolated from fecal pellets or cecal contents of ASF mice during early (30–40 days old) or adult (77–295 days old) stages, and individual ASF species were detected by species-specific qPCR. Each bar represents the diversity (number of species detected) within an individual mouse, and specific ASF species present are shown by colored squares as indicated. ASF457 (Mucispirillum schaedleri) was not detected in any of the samples.
(A–C) Each point represents an individual mouse, and the horizontal dotted line delineates the lower limit of detection of the IgE ELISA assay (0.8 ng/ml).
∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001; n.s, not significant. (p > 0.05) with an unpaired Student’s t test. See also Figure S2 and Table S2.