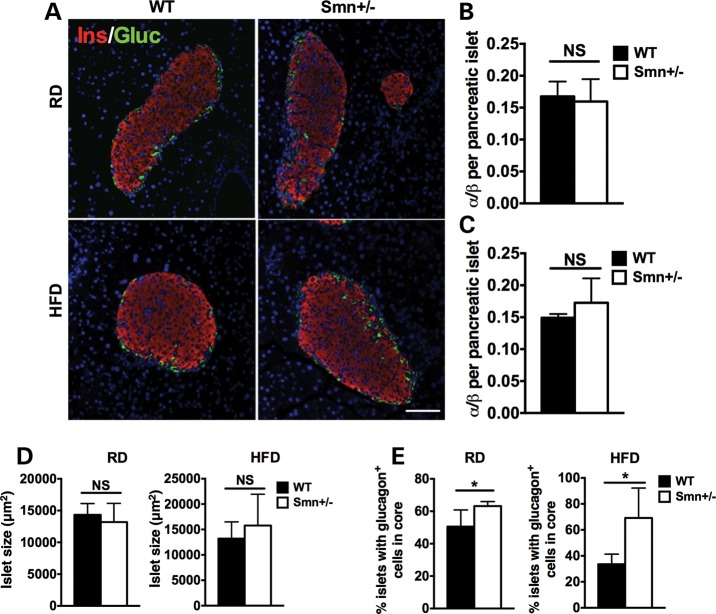
Figure 4.
Abnormal localization of pancreatic islet α-cells in Smn+/− mice is diet-independent. At P21, WT [n = 5 (RD), 4 (HFD)] and Smn+/− [n = 4 (RD and HFD)] males were placed either on an RD or HFD for 16 weeks. At the end of the 16-week diet, whole pancreas was collected and sectioned. (A) Representative images of pancreatic islets of WT and Smn+/− mice on the RD and HFD co-labeled with insulin (β-cells, red) and glucagon (α-cells, green). Scale bar = 100 μm. (B and C) Quantification of the ratio of the number of α-cells/number of β-cells per pancreatic islet in mice on the RD (B) and HFD (C) shows similar islet composition between WT and Smn+/− mice. (Data are mean ± SD; t-test; NS, not significant.) (D) Islet size of WT and Smn+/− mice on both the RD (left) and HFD (right) is not significantly different. (Data are mean ± SD; t-test; NS, not significant.) (E) Quantification of percentage of islets containing abnormally localized α-cells within the islet core demonstrates a significant increase in Smn+/− mice on both the RD (left) and HFD (right). [Data are mean ± SD; *P = 0.04 (RD) and 0.02 (HFD).]