Figure 2.
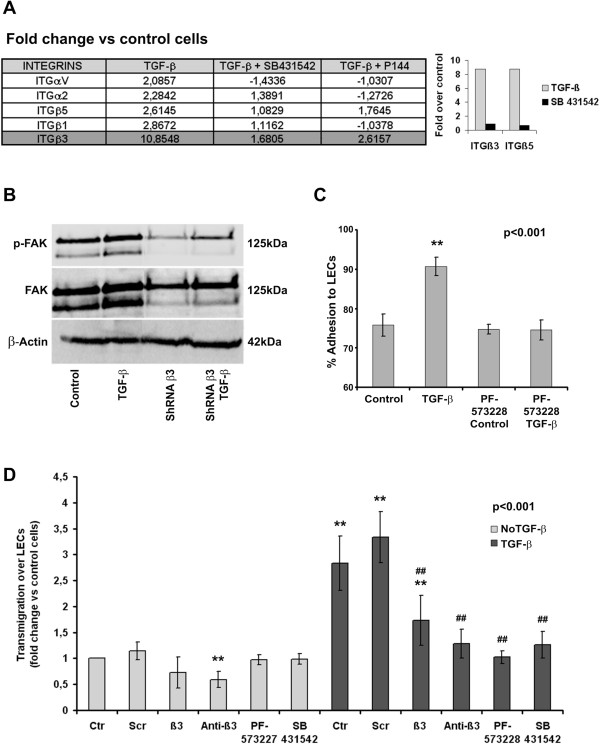
TGF-β treatment induces integrin expression, FAK phosphorylation, β3 integrin-dependent adhesion and transmigration of H157 NSCLC cells across LEC monolayers. (A) mRNA expression of several integrins in H157 cells following treatment with TGF-β and its inhibitors (fold-change with respect to untreated cells) and confirmation by real-time PCR of the differential expression of β3 and β5 integrins after exposure to TGF-β. (B) FAK phosphorylation after TGF-β treatment of β3 integrin-deficient (shRNAβ3) and β3 integrin-competent H157 NSCLC cells. (C) Adhesion of TGF-β-treated H157 cells to LEC monolayers in the presence or absence of the FAK inhibitor, PF-573228 (**p < 0.001, Student’s t-test). (D) Quantification of H157 cell transmigration across LEC monolayers in the presence of the TGF-βRI inhibitor SB431542, the FAK inhibitor PF-573228, a blocking mAb against β3 integrin (Anti-β3) and that of β3 integrin-deficient H157 clones (β3). Samples were pretreated with or without TGF-β as described in the Materials and methods (**p < 0,001 compared against non-treated cells, ## p < 0,001 compared against TGFβ-treated cells, Mann–Whitney U-test).
