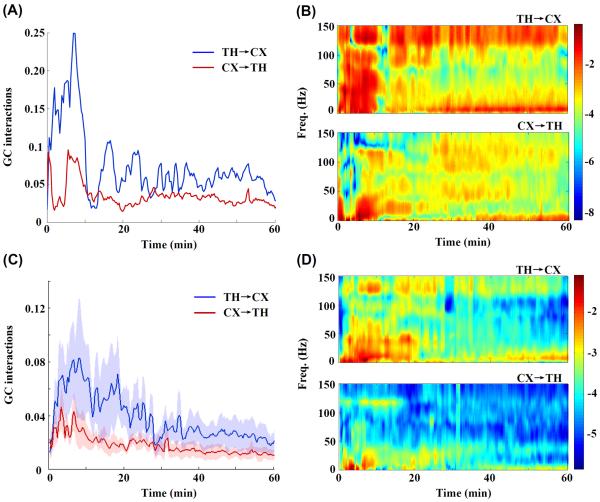
Fig. 5.
(A) The changes in GC interactions over time during to 1hr. after CA in an example rat. The blue curve shows the GC interactions from the thalamus to the cortex (TH→CX) and the red, from the cortex to the thalamus (CX→TH). Time t=0 indicates the onset of asphyxia. (B) Corresponding GC interactions in both directions for the same representative rat are plotted in the time-frequency domain, with the color index indicating the GC interactions. (C) For N=5 rats, the GC interactions (Mean±SE) as a function of time during and 1hr. after CA (Blue: TH→CX; Red: CX→TH) (D) Corresponding mean GC interactions in the time-frequency domain. In the panels B and D, the logarithm of GC interactions was used for plotting purposes to achieve better color contrast. Note that in both the domains, the GC interactions indicated asymmetric interactions between the thalamus and the cortex after CA along with higher GC interactions from the thalamus to the cortex. In addition, the dynamic thalamocortical interactions estimated by GC analysis varied with frequency.