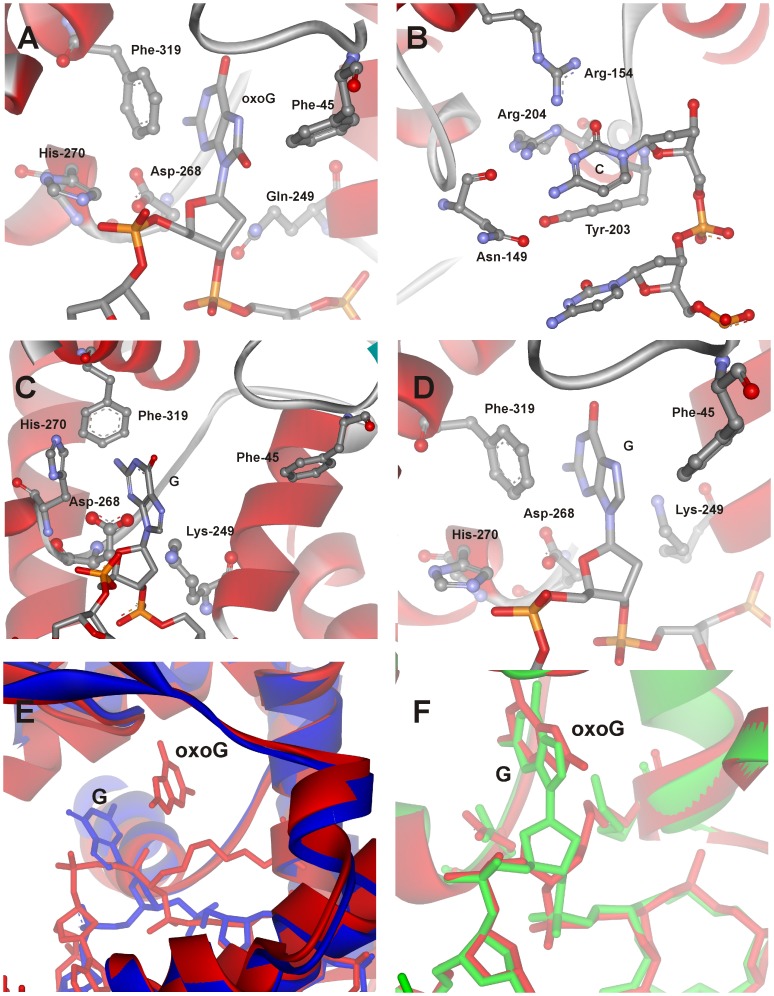
Figure 2. Close-up view of the active site of the hOGG1 complexes with damaged and undamaged DNA.
(A) The lesion recognition complex of hOGG1 bound to DNA with the oxoG base inserted in the active site (PDB ID: 1YQR, [17]), (B) specific contacts of enzyme with the cytosine which is located opposite to oxoG base (PDB ID: 1EBM, [9]), (C) the complex of hOGG1 bound to the DNA with the G base inserted in the exo-site (PDB ID: 1YQK, [17]), (D) the complex of hOGG1 bound to the DNA, with the G base inserted in the active site (PDB ID: 3IH7, [19]). The overlays of the trapped catalytic complex hOGG1/oxoG-substrate (red, 1HU0, [16]) with either (E) the complex of hOGG1 bound to DNA with the G base inserted in the exo-site (blue, 1YQK, [17]) or (F) the complex of hOGG1 bound to DNA, with the G base inserted in the active site (green, 3IH7, [19]).