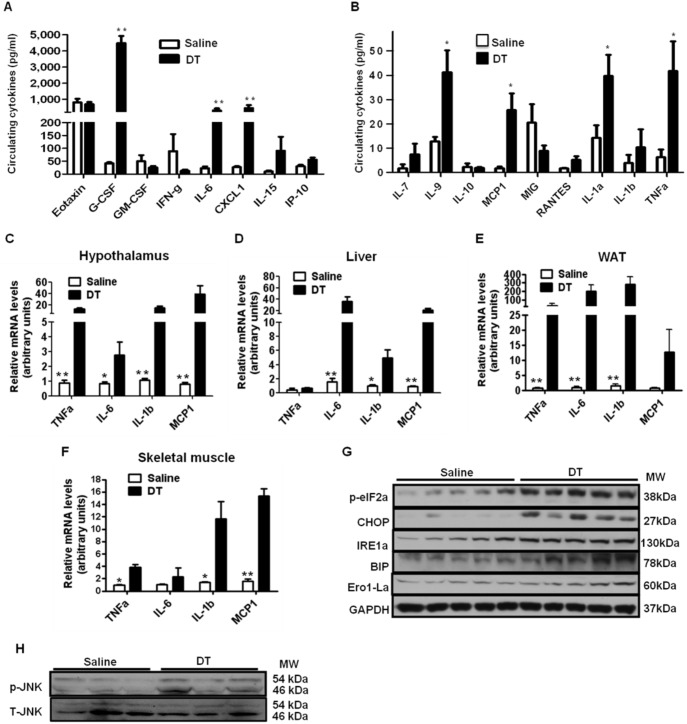
Figure 5. Macrophage depletion increases hypothalamic and systemic inflammation.
Male LysMCre/iDTR mice were i.p. injected with DT (10 ng/g) or saline for 6 days. Blood and tissue samples were collected after overnight fasting. (A and B) Serum concentrations of cytokines were measured using a mouse cytokine/chemokine array service by a commercial company (n = 8–10/group). (C–F) mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in the hypothalamus, liver, WAT, and skeletal muscle of saline or DT treated mice (n = 5 each group). (G) Protein levels related to ER-stress signaling and (H) phosphorylation of JNK were measured by Western blotting. G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor; CXCL, C-X-C motif chemokine; IL-6, interleukin-6; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; MCP1, monocyte chemotactic protein-1; MIG, monokine-induced by Interferon-gamma; RANTES, Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Asterisks denote significant differences *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. saline-treated mice.