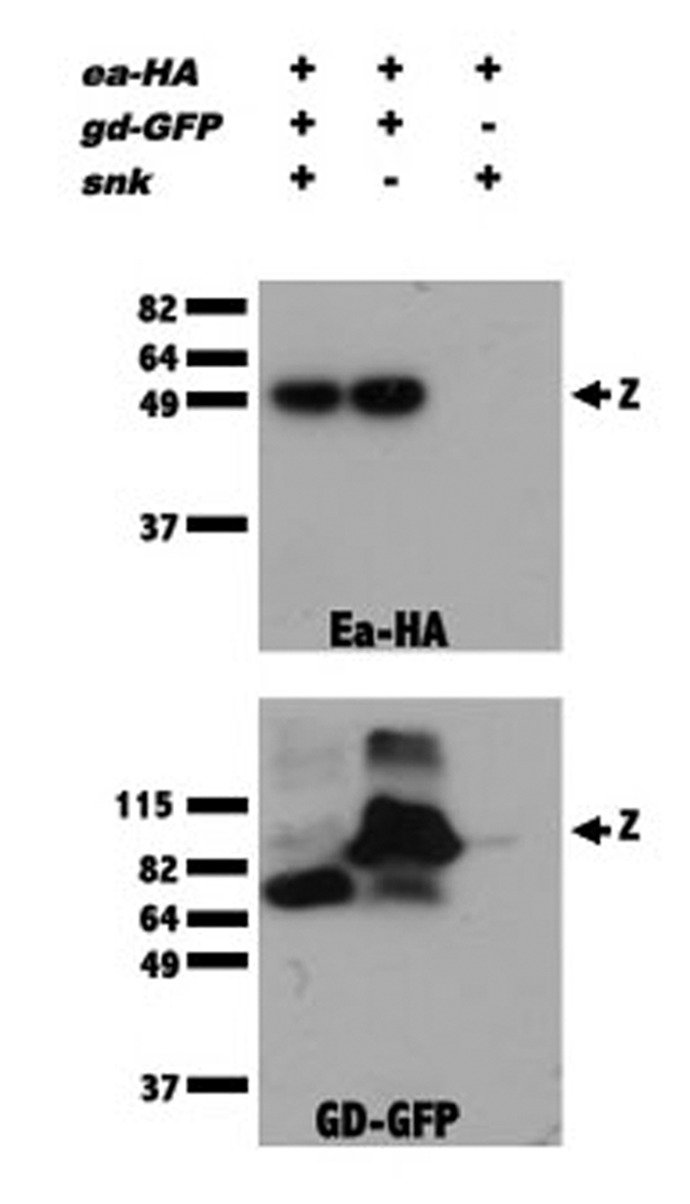
Figure 3. GD complexes with Ea in the absence of Snk. Extracts from wild-type (lanes 1, 3) or snk1/snk2-derived embryos (lane 2) expressing Ea-HA in the presence (lanes 1, 2) or absence (lane 3) of GD-GFP, were subjected to immunoprecipitation with GFP-Trap. Extracts were divided into two portions and western blot analysis was performed with anti-HA (top panel) and anti-GFP (bottom panel) antibodies. “z” indicates the position of the zymogen forms of Ea-HA (top panel) and GD-GFP (bottom panel). The ability of the GFP-Trap to bring down Ea-HA in extracts from both wild-type and snk mutant-derived extracts indicates that the association of GD with Ea does not require Snk protein. When GD-GFP and Ea-HA were co-expressed, all of the GD-GFP was processed (lane 1, bottom panel) due to a feedback mechanism in which high levels of activated Ea process GD.18,19,24 The details of the generation of embryonic extracts, precipitation with GFP-Trap and western blot analysis can be found in Cho et al.24 Details of the generation of the GD-GFP and Ea-HA transgenic lines can be found in Cho et al.25
