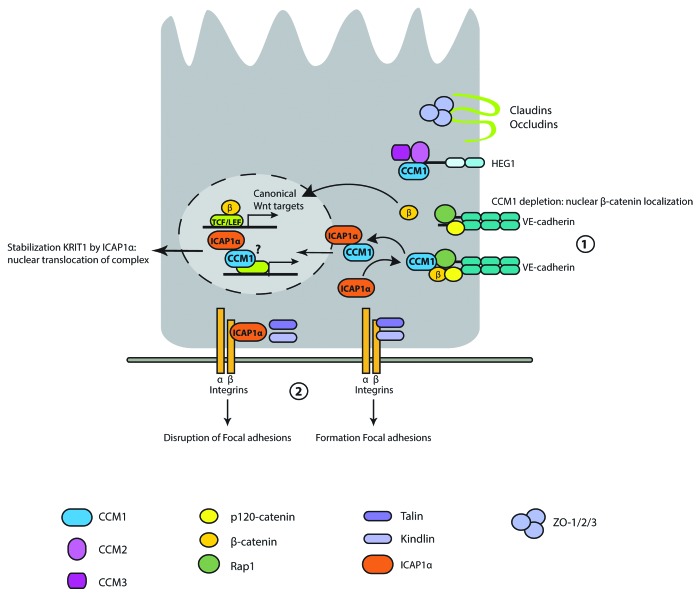
Figure 2. Molecular details of CCM1 biological function. Loss of CCM1 results in release of β-catenin from VE-cadherin, and subsequent activation of TCF/LEF-dependent transcription (1). Interaction of ICAP1 to β1-integrins disturbs focal adhesions by preventing binding of talin and kindlin. CCM1 inhibits binding of ICAP1 to β1-integrins and ICAP1 stabilizes CCM1 followed by nuclear translocation of the complex (2). CCM1 is located to the plasma membrane through interaction with the HEG1 transmembrane receptor.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.