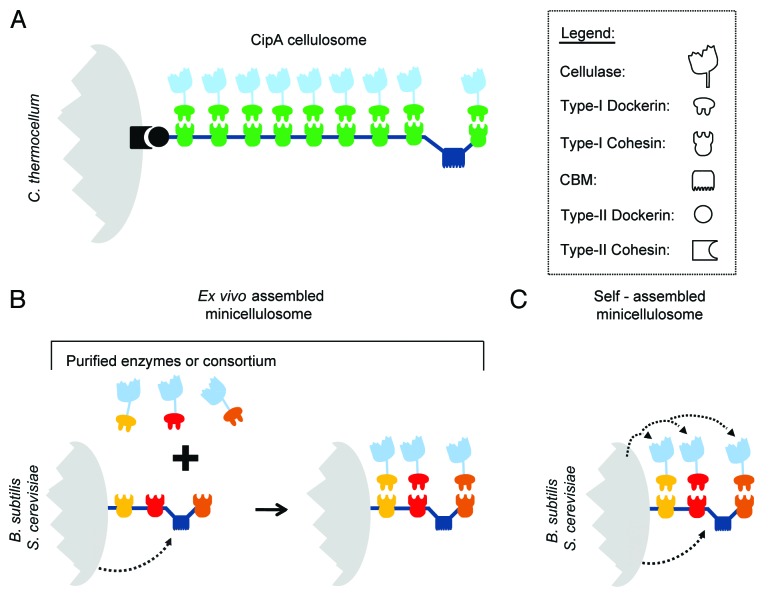
Figure 3. The prototypical CipA cellulosome and methods used to recombinantly display miniaturized cellulosomes (minicellulosomes). (A) Architecture of the prototypical CipA cellulosome produced by C. thermocellum. It houses 9 cellulases enzymes that are bound to the central scaffoldin protein, CipA.23 Binding is mediated by type-I cohesin modules within CipA that interact with sub-nanomolar affinity with type-I dockerin modules present in the cellulases. CipA also contains a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM) that tethers the cellulosome complex to its substrate, as well as a type-II dockerin module located at its C-terminus that anchors the cellulosome complex to the cohesin module of cell wall associated proteins. (B) Ex vivo approach used to display minicellulosomes on the surfaces of B. subtilis or S. cerevisiae. The microbes secrete and display a scaffoldin protein that is displayed on their surface. Cellulase enzymes containing the appropriate type-1 dockerin module are incubated with the cells to construct the minicellulosome. The enzymes that are added to the cells are either purified enzymes or secreted by other microbes as part of a microbial consortium. Distinct colors are used to indicate species-specific type-1 dockerin and cohesin domains that selectively interact with one another to construct the minicellulosome. (C) Self-assembled approach used to display minicellulosomes on the surfaces of B. subtilis or S. cerevisiae. All of the components of the minicellulosome (scaffoldin and enzymes) are produced by the microbe and spontaneously assemble on the cell surface.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.