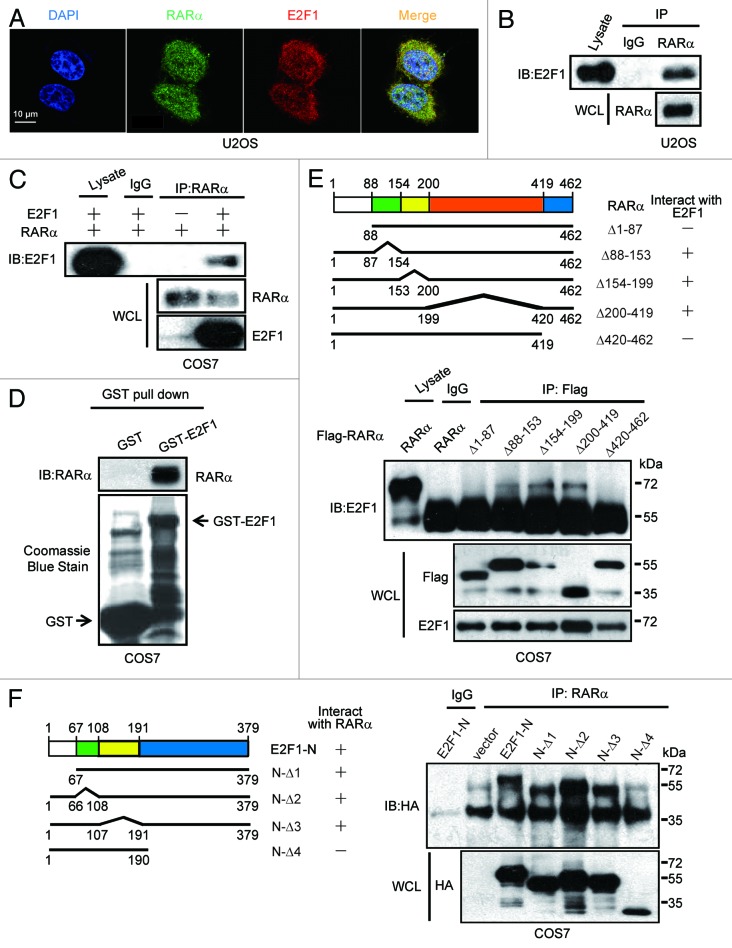
Figure 5.
Interaction between E2F1 and RARα. (A) Colocalization of endogenous E2F1 and RARα. The subcellular localization of E2F1 and RARα in U2OS cells was assessed by immunofluorescence. (B) Interaction between endogenous E2F1 and RARα. U2OS cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-RARα followed by immunoblotting with anti-E2F1. WCL, whole-cell lysates. (C) Interaction between ectopical expressions of E2F1 and RARα. COS7 cells were transfected with RARα and E2F1; 48 h later, cell lysates were coprecipitation with anti-RARα and immunoblotting with anti-E2F1 or anti-RARα. (D) Interaction between E2F1 and RARα in vitro. GST or GST-E2F1 fusion proteins were used in a pull-down assay with in vitro translated. (E) The N terminus and C terminus of RARα are both required for E2F1 binding. COS7 cells transfected with HA-E2F1 along with different deletion mutants of Flag-RARα were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag and immunoblotted with anti-E2F1 or anti-Flag (lower). Different deletion mutants of RARα were presented (upper). (F) N terminus of E2F1 involved in the interaction with RARα. RARα and E2F1-N mutants were transfected into COS7 cells followed by immunoprecipitated with anti-RARα and immunoblotted with anti-HA (right). Different E2F1-N deletion mutant constructs were illustrated (left).