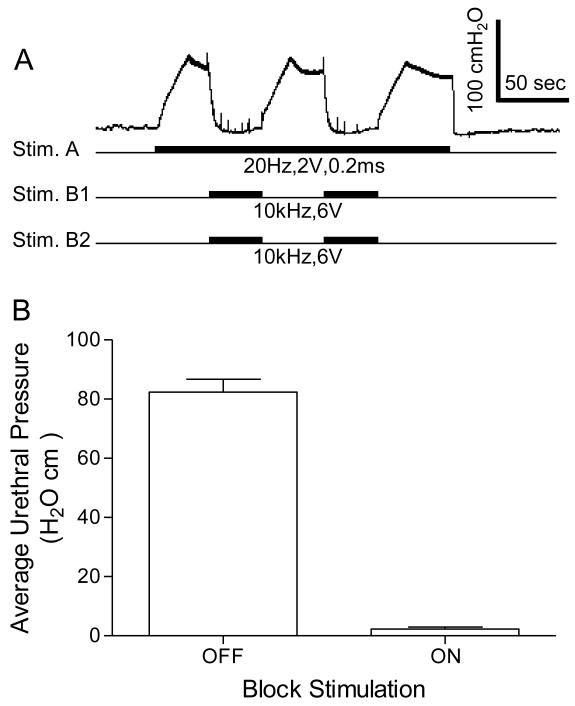
Fig.5.
High frequency biphasic stimulation of the pudendal nerves bilaterally completely blocked the increase in urethral pressure induced by unilateral pudendal nerve stimulation. A. Records from one female cat showing the representative block of the response elicited by Stim. A during bilateral pudendal nerve stimulation (Stim. B1 and Stim. B2). High frequency stimulation delivered to Stim. B1 and Stim. B2 (see Fig.1B) completely reduced the urethral pressure induced by Stim. A. The black bars under pressure trace indicate the stimulation duration. The Y-calibration bar indicates the urethral pressure in 100 cmH2O and the X-calibration bar indicates the time in 50 seconds. B. Average urethral pressure induced by Stim. A when the high frequency stimulation was either on or off. Stim. A: frequency 20 Hz, pulse width 0.2 ms, intensity 2-5 V. Stim. B1/B2: frequency 6-15 kHz, intensity 6-10 V. N = 4 cats. A total of 8 tests were performed in 4 cats with 1-3 tests in each cat.