Figure 4. Characterization of TEBV in vivo.
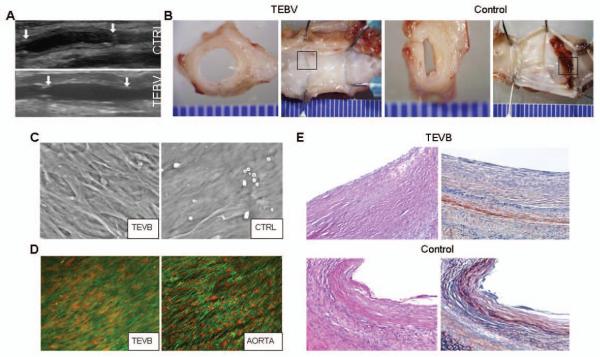
(A) Duplex ultrasound of TEBV and control grafts (CTRL) 2wk following implantation as interposition grafts within rabbit infra-renal aorta. (B) Representative gross examination of TEBV and control graft 8wk after implantation (views of the mid-graft cut transversely and the entire graft splayed open longitudinally). (C) Scanning electron micrograph of the luminal surface of an ASC-seeded TEVB and unseeded control graft (CTRL) 8wk after implantation. (D) Laser confocal micrograph (actin stain, green; nuclear stain, red) of a TEVB 8wk after implantation demonstrates the presence of a confluent, aligned layer of cells on the luminal surface of the graft. For comparison, staining of the adjacent native aorta is shown. (E) Photomicrographs of grafts 8wks after implantation (H&E, left; PTAH, right). The TEBV is free of significant fibrin formation on its luminal surface (fibrin stains red upon staining with PTAH). Representative results are shown from one TEBV and one control graft. Similar results were obtained from another 4 animals.
