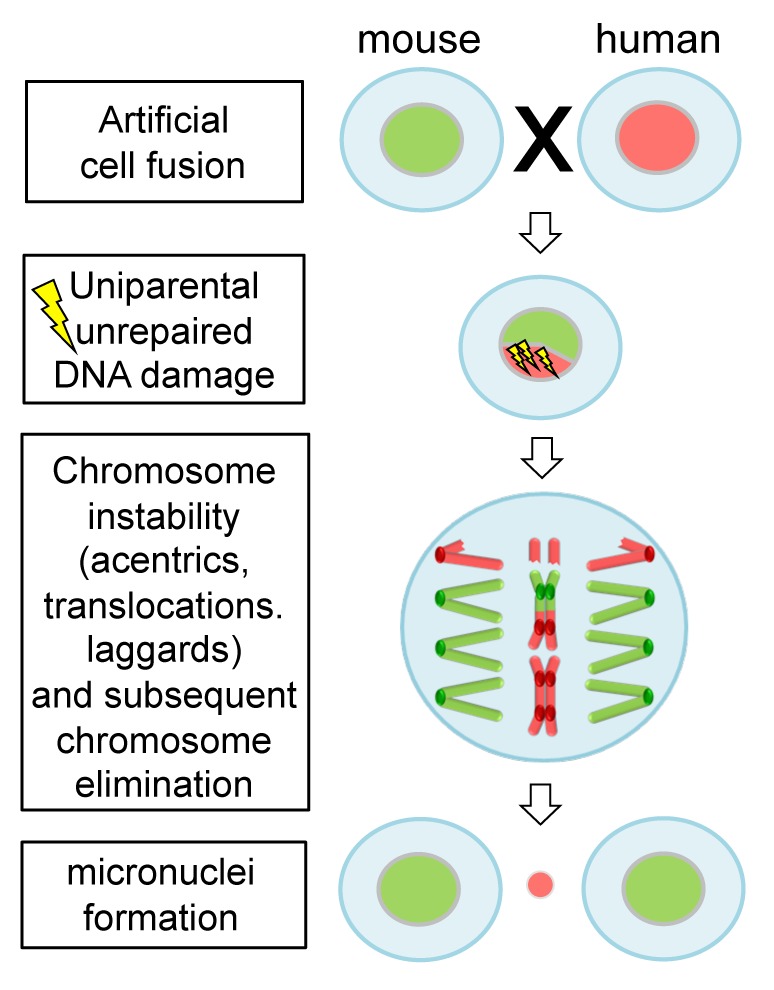
Figure 1. Unrepaired DNA damage facilitates elimination of uniparental chromosomes in interspecific hybrid cells. Human–mouse hybrid cells are formed by artificial cell fusion. Deficiency in DNA damage repair of human chromosomes likely results in structural chromosome aberrations, such as acentrics, dicentrics and translocations. Consequently, progressive elimination of human chromosomes occurs.
