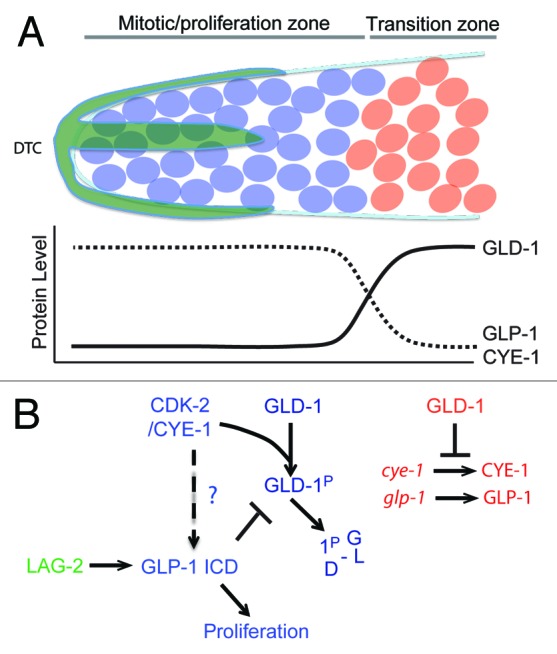
Figure 4. (A) Transition from mitosis into meiosis in C.elegans germline. The Distal Tip Cell (DTC in green) caps the distal end of the germline and induces mitotic proliferation (blue). Beyond the reach of the DTC Notch signaling, germ cells transition into the differentiation zone in a GLD-1 dependent manner, where they undergo meiosis (red). (B) Model for Cyclin E in maintenance of germ stem-cell fate in C. elegans. The boundary between the proliferative and transition zones is maintained by 2 mutual negative regulations: CDK-2/ CYE-1 and GLP-1 inhibit accumulation of GLD-1 in the mitotic proliferation zone, while GLD-1 represses the translation of cye-1 and glp-1 transcripts in the transition zone. It remains to be seen if CYE-1 can maintain proliferation zone by enhancing GLP-1 ICD induction in the similar way it does in vulval development.
