Fig. 6.
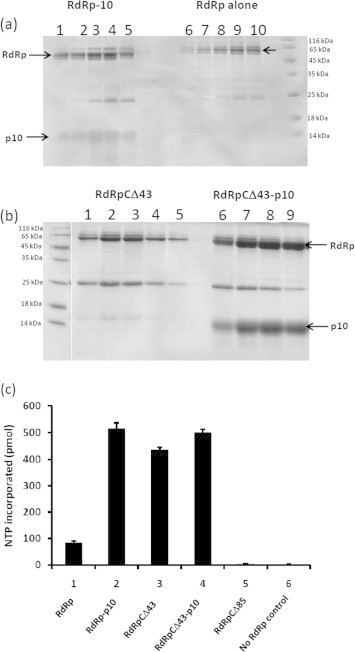
Purification of RdRp, RdRpCΔ43, RdRp-p10 complex and RdRpCΔ43-p10 complex and in vitro RdRp assay: Untagged RdRp and RdRp CΔ43 were coexpressed with 6xHis tagged p10 and purified by Ni–NTA chromatography. The RdRp and its mutant that formed complex with p10 was separated on SDS–PAGE and detected with coomassie brilliant blue staining. For the purification of RdRp alone and RdRpCΔ43 alone, they were cloned in pET22b vector to give C-terminal His tag. These clones were expressed and purified as described in methods section. (a) RdRp–p10 complex (lanes 1–5) and RdRp alone (lanes 6–10); (b) RdRpCΔ43 (lanes 1–5) and RdRpCΔ43–p10 complex (lanes 6–9). (c) In vitro RdRp assay: The reaction products were analyzed by filter binding assay, RdRp assay with RdRp alone bar 1; RdRp–p10 complex bar 2; RdRpCΔ43 bar 3; RdRpCΔ43–p10 bar 4; RdRpCΔ85 bar 5 and without RdRp control, bar 6.
