Fig. 3.
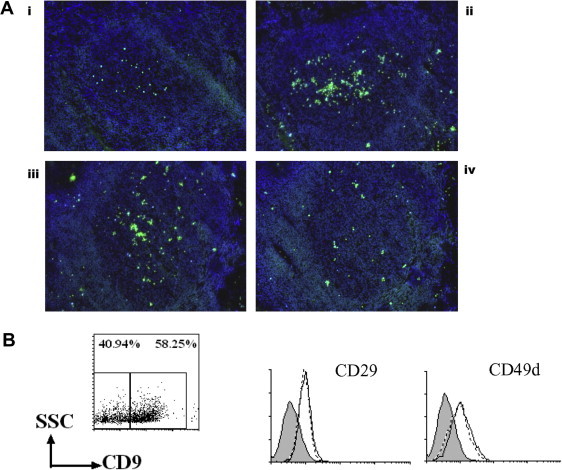
The binding of CD9+ GC-B cells to the tonsillar tissue section is inhibited by the anti-integrin β1 antibody. (A) CD9+ and CD9− GC-B cells were internally labeled with Calcein-AM and then applied to the tonsillar tissue sections. Slides were then examined under a fluorescent microscope: (i) CD9− GC-B cells, (ii) CD9+ GC-B cells, (iii) CD9+ GC-B cells preincubated with an isotype control antibody, and (iv) CD9+ GC-B cells preincubated with an anti-integrin β1 antibody. Representative data from two independent experiments are shown. (B) GC-B cells were stained with anti-CD9, anti-CD29, and CD49d. Histograms with broken and solid lines indicate the expression levels of CD29 and CD49d in CD9− GC-B cells and CD9+ GC-B cells, respectively. Filled histograms indicate isotype control.
