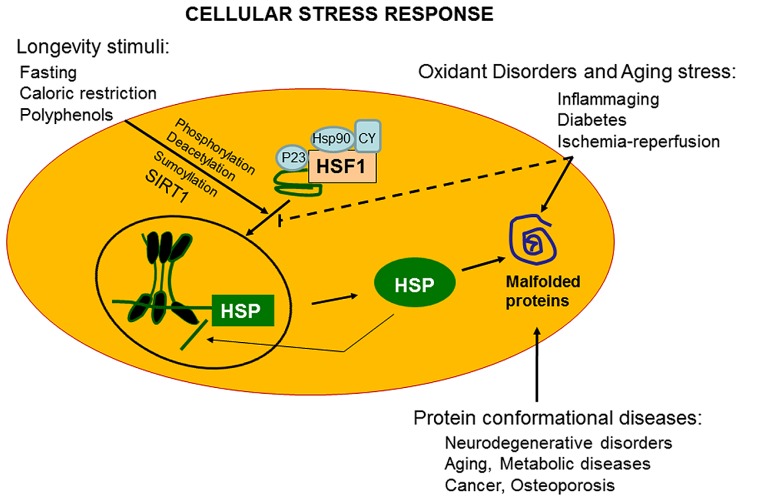
FIGURE 1.
Vitagenes and the pathway of cellular stress response. Misfolded proteins cumulating in response to proteotoxic stresses trigger the cellular stress response. Hsps that are normally bound to HSF1, maintaining it in a repressed state before stress, are titrate away by damaged or misfolded proteins with resulting HSF-1 activation. Multi-step activation of HSF1 involves post-translational modifications, such as hyperphosphorylation, deacetylation, or sumoylation, which allow HSF1 to trimerize, translocate into the nucleus, and bind to heat shock elements (HSEs) in the promoter regions of its target Hsp genes. Nutritional anti-oxidants, are able to activate vitagenes, such as heme oxygenase, Hsp70, thioredoxin reductase and sirtuins which represent an integrated system for cellular stress tolerance. Activation of vitagene system, with up-regulation of HO-1, thioredoxin, GSH, and sirtuin, results in reduction of pro-oxidant conditions. During inflammaging, including aged-associated pathologies, such as Alzheimer’s disease and osteoporosis, a gradual decline in potency of the heat shock response occur and this may prevent repair of protein damage, leading to degeneration and cell death of critical parenchymal cells.