Figure 6.
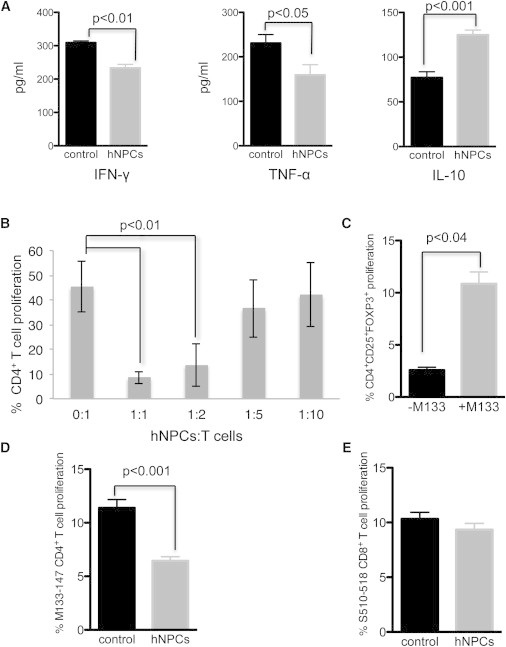
hNPCs Modulate T Cell Responses
(A) T cells were isolated from draining cervical lymph nodes of control and hNPC-transplanted mice at 3 weeks pt, stimulated with M133–144 viral peptide, and their secretion of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-10 was determined by ELISA after 48 hr of culture. IFN-γ and TNF-α secretion was lower and IL-10 secretion higher in hNPC-treated mice.
(B) hNPCs were cocultured with activated T cells at the indicated ratios, and T cell proliferation was determined by eFluor 670 staining. Results demonstrated that hNPCs suppressed T cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner.
(C) Coculture of hNPCs with activated T cells either in the presence or absence of the immunodominant CD4 viral peptide (M133–147) revealed increased numbers of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ T cells when viral peptide was included.
(D) Coculture with hNPCs inhibited proliferation (p < 0.001) of M133–147 CD4+ T cells.
(E) S510–518-specific CD8+ T cells were not affected following coculture with hNPCs.
Data are representative of at least two independent experiments with a minimum of three mice per group; data are presented as average ± SEM. Mann-Whitney t tests were used to determine the p values in (A) and (B); paired t tests were used to determine the p values in (C) to (E).
