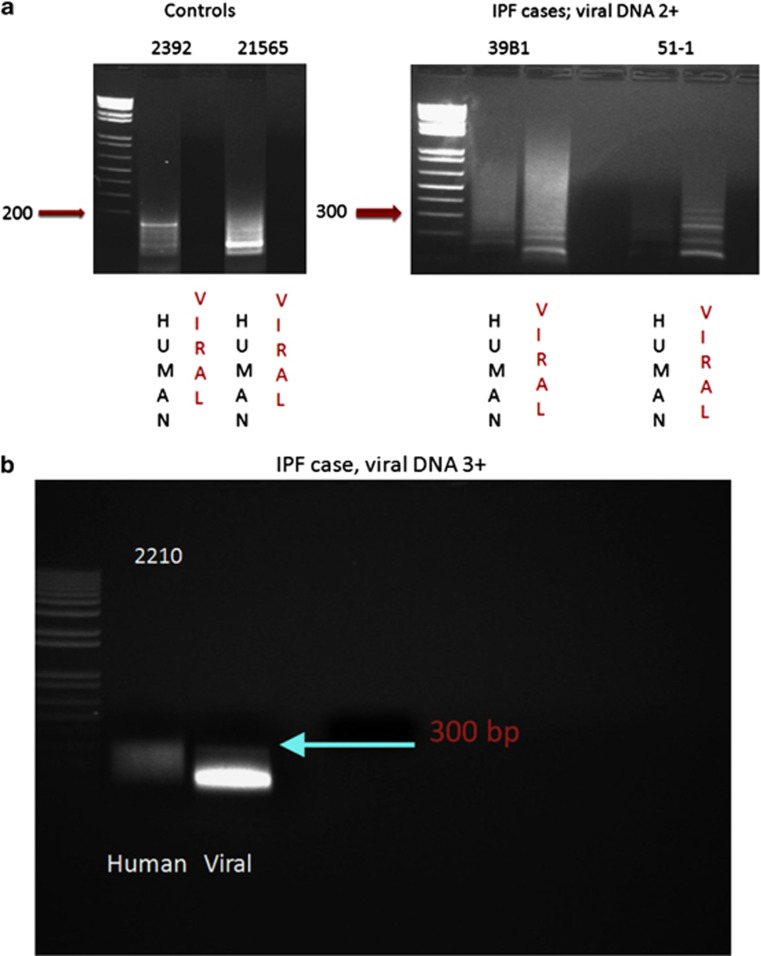
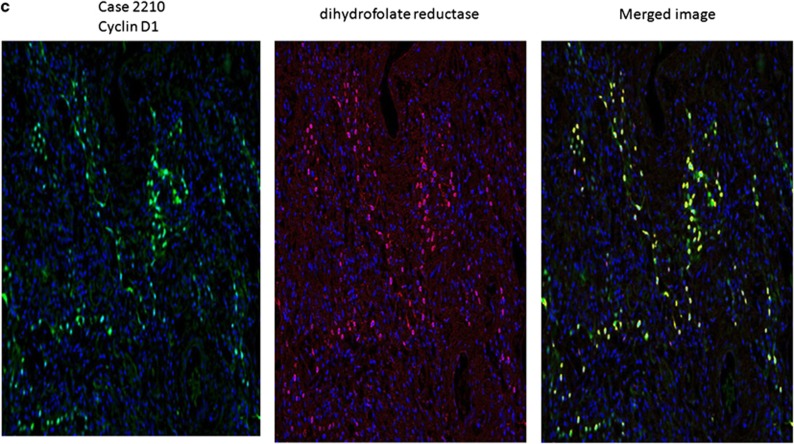
Figure 4.
Detection of viral cyclin RNA using RT-PCR analysis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. In a, it is evident that samples 2392 (negative for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis) and 21 565 (histologically normal area of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis case with no detectable viral DNA) showed only human cyclin D1 cDNA amplicons after RT-PCR (viral amplicon 290 nucleotides and human amplicon 180 nucleotides). In comparison, the RNA extracted from two cases of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with active fibrosis and 2+ viral DNA (39B1 and 51-1) showed primarily viral cyclin D1 amplicons after RT-PCR analysis. b shows that in an idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis case with 3+ herpesvirus saimiri DNA (2210), only viral cyclin D RNA sequence is amplified and that the band intensity is greater than that for the 2+ viral cases shown in a. c shows the strong expression of cyclin D using immunohistochemistry in case 2210 plus the strong co-expression of cyclin D1 (fluorescent green) and dihydrofolate reductase (fluorescent red) with the merged image showing co-expression as fluorescent yellow.