Figure 1.
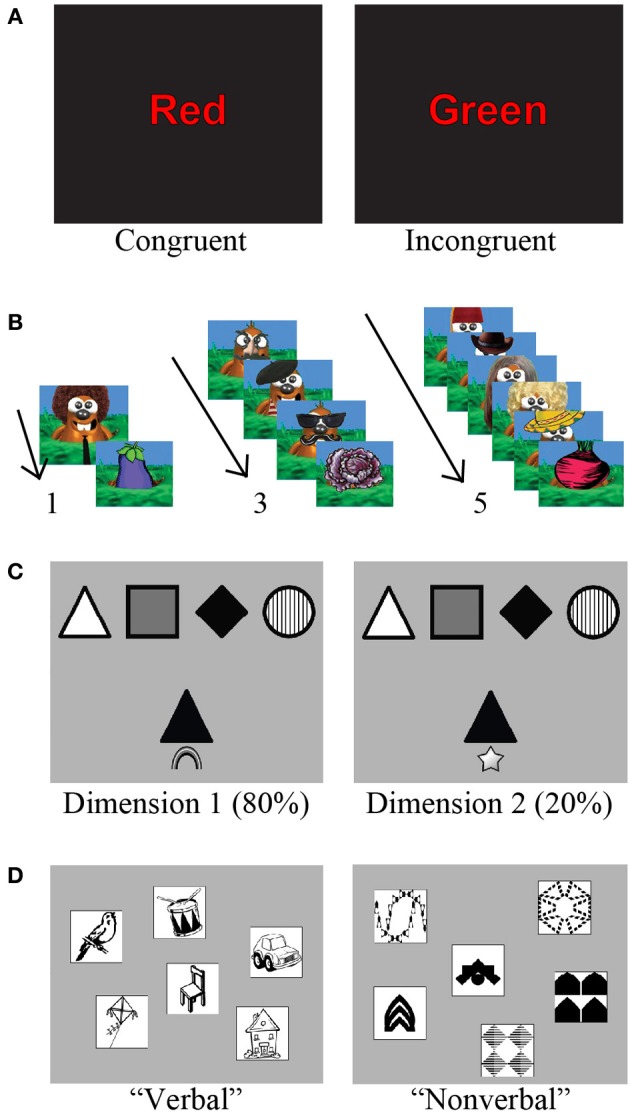
Examples of the cognitive control battery. (A) For the Stroop task, participants had to respond by indicating the ink color on congruent (left) or incongruent (right) trials. (B) “Whack-a-mole” Go/No-Go task. Children were instructed to press a button as quickly as possible when a cartoon mole appeared (Go trial), but to avoid pressing the button when a vegetable appeared (No-Go trial). No-Go trials were preceded by 1, 3, or 5 Go trials (Adapted from Shapiro et al., 2013). (C) The two gray squares each represent a touch-screen display in the Visually-Cued Card Sort (VCCS). A sample of the target cards can be seen at the top of the screen, while the test card is below. The visual cue appears just below the test card, with a rainbow indicating to sort by color (left panel), and a star indicating to sort by shape (right panel). (D) The two gray squares each represent a touch-screen display in the for the verbal and non-verbal Self-Ordered Pointing Test (SOPT), respectively. Images represent a trial with 6 objects, the most difficult condition of the task.
