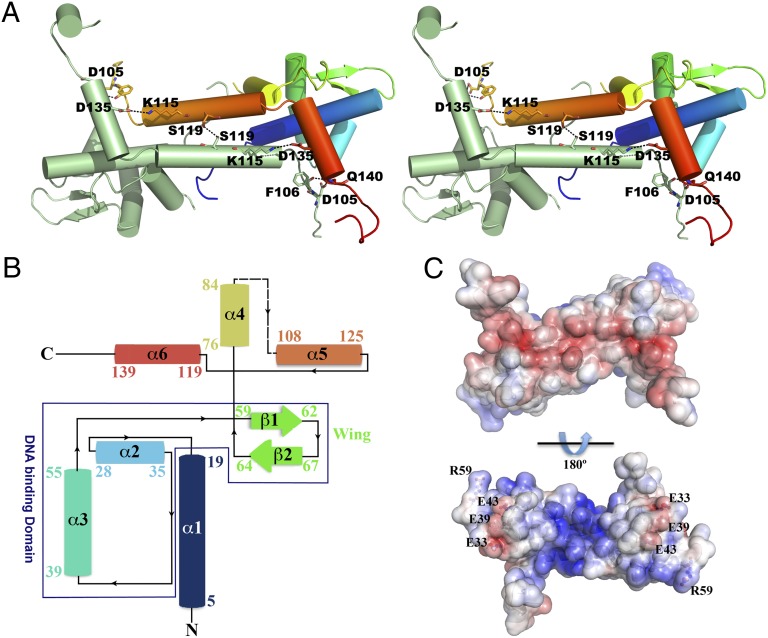
Fig. 2.
The 3D structure of T. potens IscR. (A) Stereoscopic view of the biologically active apo-IscRTp dimer, highlighting important residues (represented as sticks) at the dimerization interface. One of the monomers is colored from N- (blue) to C-terminal (red), with highlighted residues color-coded (nitrogen blue, oxygen red). Hydrogen bonds are represented as dashed lines. (B) Topology diagram of the apo-IscRTp monomer. Secondary structure element colors match those of A. (C) Solid-surface representation of the apo-IscRTp dimer, with mapped electrostatic surface potential contoured from +5 (blue) to −5 (red) kbTe−1 [kb, Boltzmann’s constant; T, temperature (K); e, charge of an electron].