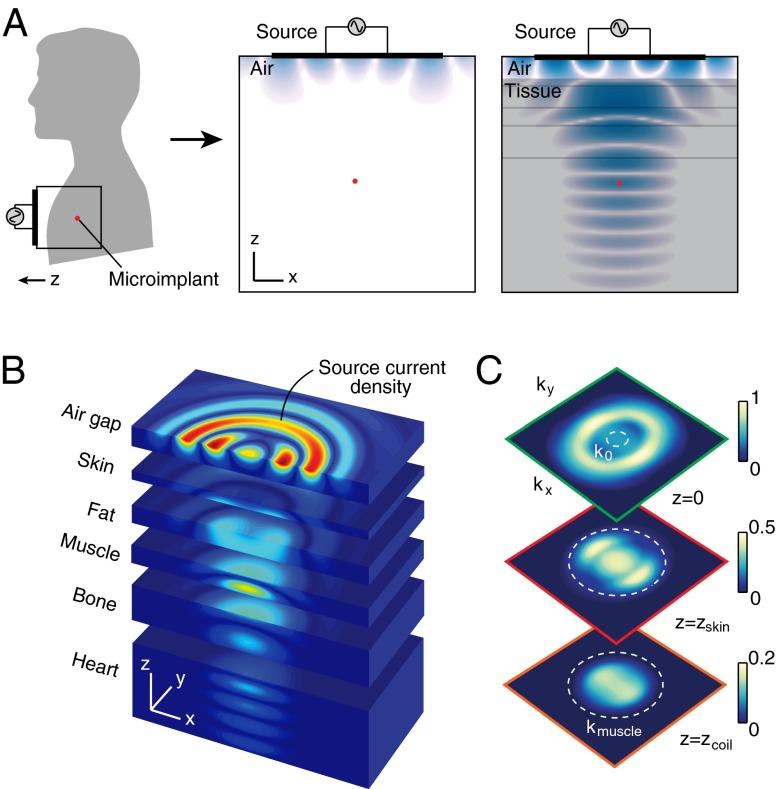
Fig. 1.
Wireless energy transfer to a subwavelength coil. (A) Schematic for power transfer to a subwavelength coil mounted on the surface of the heart. Magnetic field (time snapshot , logarithmic scale) (Right) in air and (Left) coupled into multilayered tissue. The source is solved using the optimization methodology for maximum power transfer through tissue multilayers at 1.6 GHz. The coil (red dot) is 5 cm from the source. (B) Expanded view of the magnetic field in tissue multilayers, revealing propagating waves that converge on the coil (linear scale). (C) Spatial frequency spectra at depth planes corresponding to the source (green box), the skin surface (red box, cm), and coil (orange box, cm). , wavenumber in air; , wavenumber in muscle tissue.