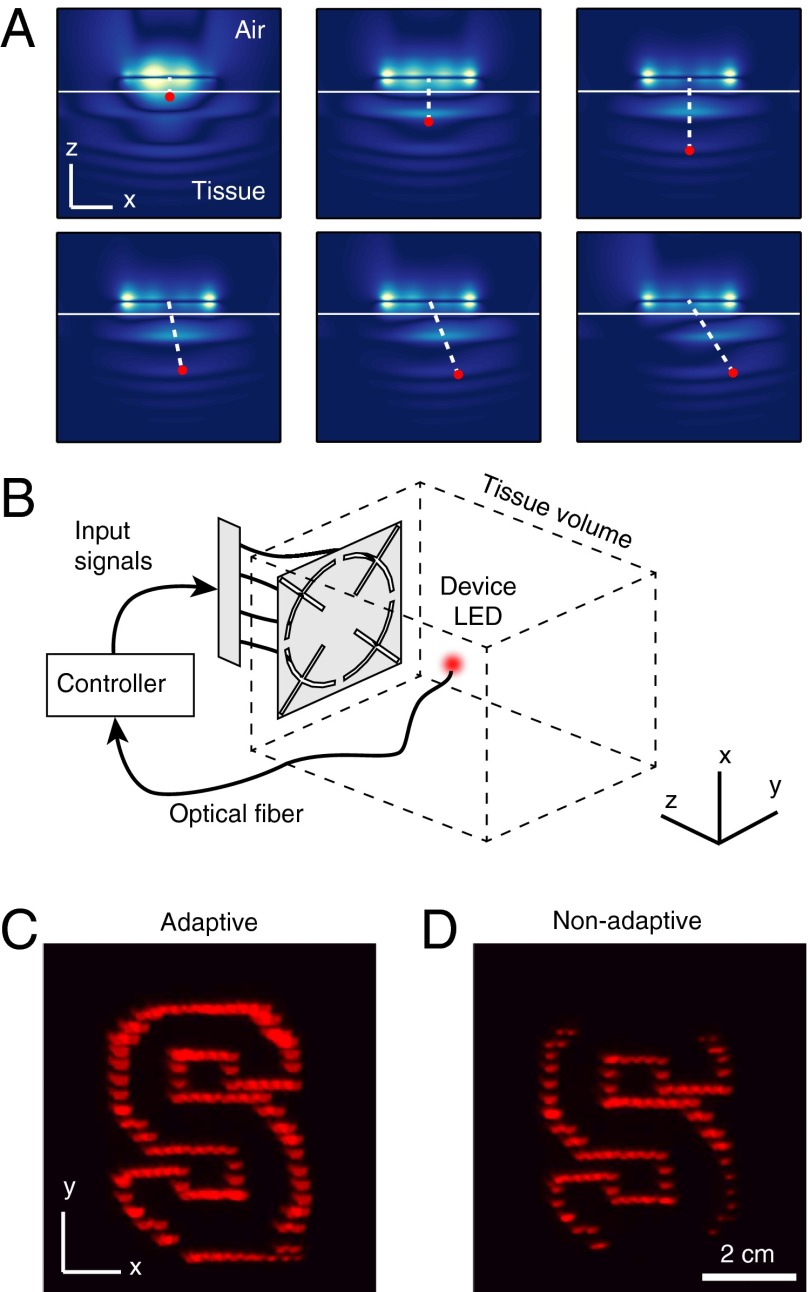
Fig. 4.
Real-time dynamic focusing. (A) Field patterns with spatially shifted focal points designed by adjusting the relative phases between the port signals. (B) Experimental setup for measuring the transferred power to a moving device in a liquid solution whose properties mimic muscle tissue. (C) Strobed position of the LED as the wireless device moves in an S-shaped trajectory. A real-time control algorithm dynamically tracks for motion. (D) Same as C, but without dynamic focusing; the field pattern is static and focused at the center.