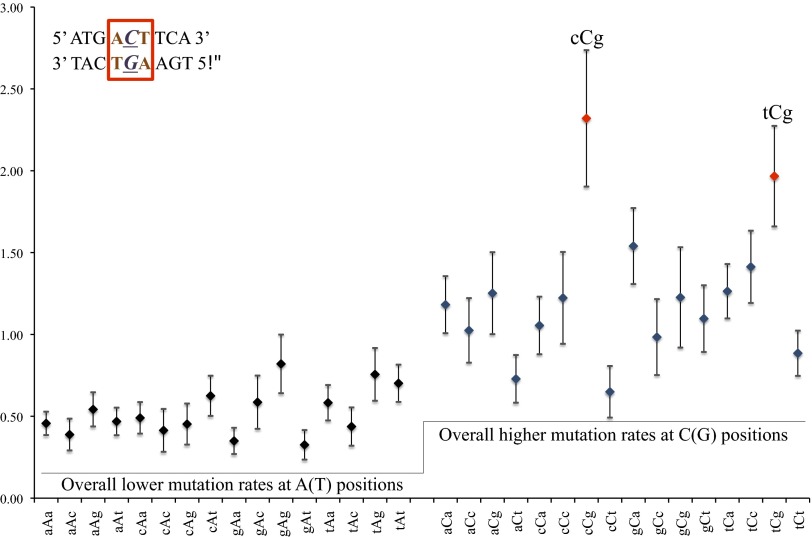
Fig. 5.
(y axis) Relative mutation rate. (x axis) Neighbor environment. Neighbor-dependent mutation rate is defined as the effects of immediate flanking nucleotides (e.g., bases a and t in an aCt environment) on mutation rate at base of interest (base C in an aCt environment). Environment classes represent mutation rates regardless of strand orientation (aCt class includes overall mutation rate at aCt and aGt positions). Average mutation rate of 1.24 (1.11 when excluding cCg and tCg contexts) at C/G bases shows clear overall elevation over a corresponding rate of 0.52 at A/T bases. In addition, two environments (cCg and tCg) show additional elevations in mutation rate.