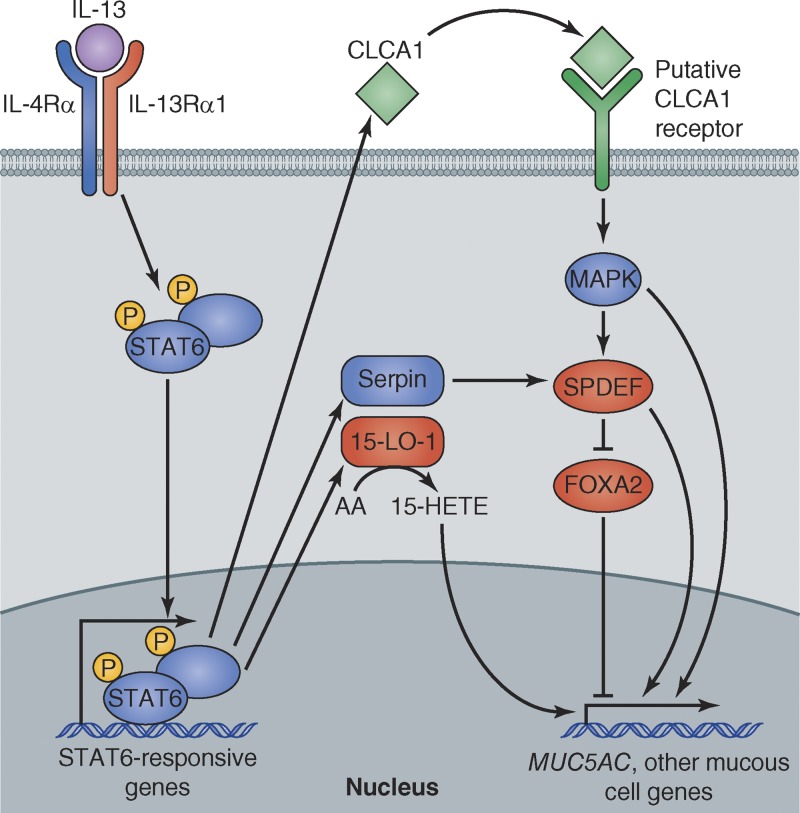
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of IL-13–induced mucous metaplasia. IL-13 binds to its receptor on the surface of mucous cell progenitors (e.g., club cells) leading to phosphorylation of STAT6 and translocation of STAT6 heterodimers to the nucleus, where they bind to promoters of STAT6-responsive genes. STAT6-dependent processes that contribute to mucous metaplasia include a CLCA1-dependent pathway, a Serpin-dependent pathway, and a 15-lipoxygenase-1–dependent pathway. The transcription factor SPDEF is a master regulator of mucous cell differentiation. It inhibits FOXA2, which represses mucous cell differentiation, and activates transcription of other genes that are expressed in mucous cells.