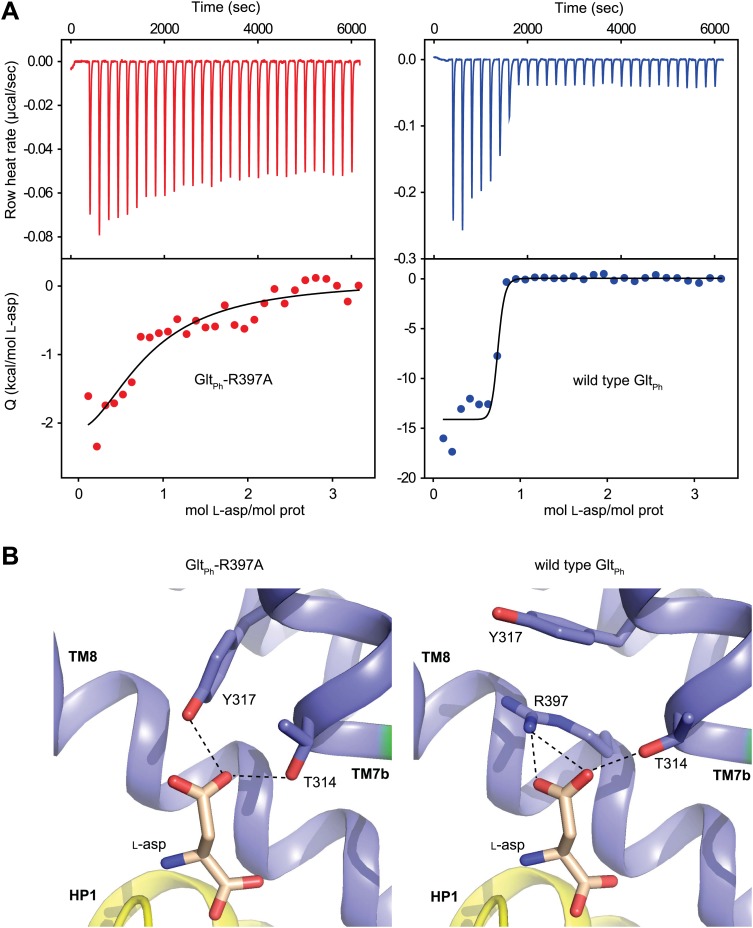
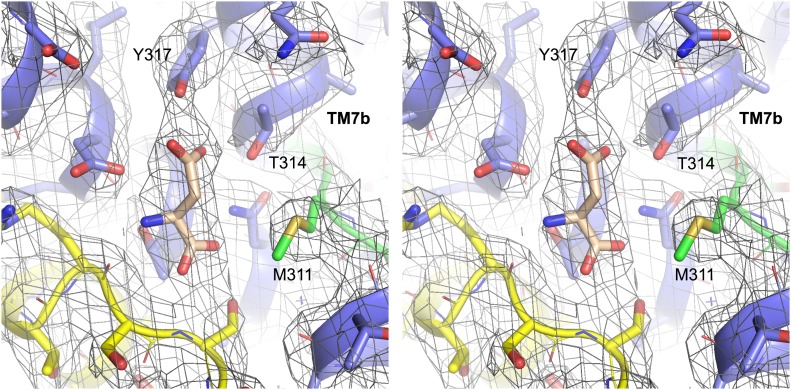
Figure 1. Substrate binding to GltPh-R397A.
(A) Raw binding heat rates measured by isothermal titration calorimetry (top) and binding isotherms (bottom) obtained for GltPh-R397A (left) and wild type GltPh (right) at 25°C in the presence of 100 mM NaCl. The solid lines through the data are fits to the independent binding sites model with the following parameters for GltPh-R397A and wild type GltPh, respectively: enthalpy change (ΔH) of −3.2 and −14.3 kcal/mol; the apparent number of binding sites (n) of 0.8 and 0.7 per monomer; dissociation constant (Kd) of 6.6 µM and 27 nM. Note that L-asp binding to the wild type transporter is too tight at 100 mM NaCl to be accurately measured in this experiment. The binding Kd has been estimated to be ∼1 nM (Boudker et al., 2007). (B) L-asp binding site in GltPh-R397A (left) and wild type GltPh (right). L-asp and residues coordinating the side chain carboxylate are shown as sticks with carbon atoms colored light brown and blue, respectively. Potential hydrogen bonds (distances less than 3.5 Å) between the L-asp side chain carboxylate and transporter residues are shown as dashed lines. Note that Y317, which forms cation-π interactions with guanidium group of R397 in wild type GltPh, interacts directly with L-asp in GltPh-R397A.