FIGURE 3.
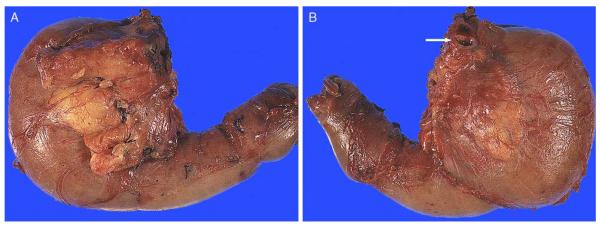
(A) Anterior surface. Anterior surface of a PD typically contains abundant adipose tissue and is convex in appearance. Transition of the pancreatic head to the duodenal wall is also often more irregular, showing a palpable sharp edge due to the overriding pancreatic parenchyma. (B) Posterior surface. In contrast with the anterior surface, the posterior surface is relatively flat, smooth, and glistening. Transition from the pancreatic head to the duodenal wall (pancreaticoduodenal junction) is fairly smooth as well, with the pancreaticoduodenal “groove” only barely identifiable. Note the CBD orifice at the superior edge, at the plateau (arrow).
