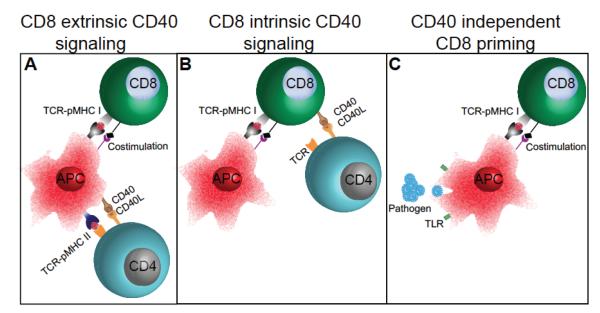
FIGURE 1.
Role of the CD40–CD40L pathway during the CD8 primary response. Multiple models have proposed to explain the role of the CD40–CD40L pathway in mediating CD4 help to CD8 T cells. (A) The first model suggests that CD40L-bearing CD4 T cells fully activate or license APC by engaging CD40 on APC. Such licensed or highly activated DC can then prime CD8 T cells. (B) The second model suggests that CD8 T cells either simultaneously or sequentially interact with antigen-presenting cells and CD40L-expressing CD4 T cells, which permits full activation of CD8 T cells. (C) However, in acute infectious disease models, CD4 T-cell help is dispensable for the CD8 primary response and CD8-intrinsic CD40 signaling plays a minimal role in mediating CD8-response development. For certain infections, even CD8-extrinsic CD40 signaling is not required for optimal CD8 response. This may be due to pathogen-mediated activation of TLRs on APCs and consequent inflammatory milieu, which may overcome the need for CD4 help or CD40 signaling.