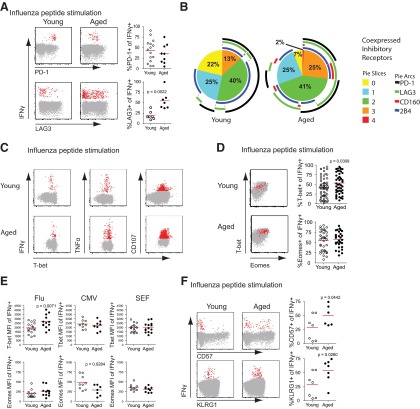
Figure 6. T-bet and Eomes expression on functional CD8 T cells in young and aged individuals.
(A) Expression of inhinbitory receptors PD-1 and LAG3 in representative young and aged subjects (Mann-Whitney; PD-1, n=15 young and 9 aged; LAG3, n=7 young and aged). (B) Coexpression of inhibitory receptors on influenza virus-specific CD8 T cells using SPICE analysis. (C) Coexpression of T-bet with IFN-γ, TNF-α, or CD107 as effector functions of CD8 T cells in young and aged individuals in response to influenza virus peptides. (D) Overlay of T-bet and Eomes expression of influenza-specific (red) and total CD8 T cells (gray) with relative expression of T-bet and Eomes in influenza-specific CD8 T cells from young and aged subjects (Mann-Whitney; T-bet, n=61 young and 48 aged; Eomes, n=36 young and 30 aged). (E) Pooled data showing T-bet and Eomes levels (MFI) in CD8 T cells producing IFN-γ in response to influenza (Mann-Whitney; n=17 young and 13 aged T-bet; n=13 young and 11 aged Eomes), CMV peptides (n=9 young and 8 aged T-bet; n=9 young and 7 aged Eomes), or SEF superantigen (n=16 young and 14 aged T-bet; n=10 young and 9 aged Eomes). (F) CD8 T cell function relative to CD57 and KLRG1 expression in CD8 T cells from young and aged subjects responding to influenza peptides. Staining of CD57 and KLRG1 on cells making IFN-γ and relative percentages of CD57 (n=7 young and 6 aged) or KLRG1 (n=7 young and 7 aged) expression on the same cells (Mann-Whitney).