Figure 2.
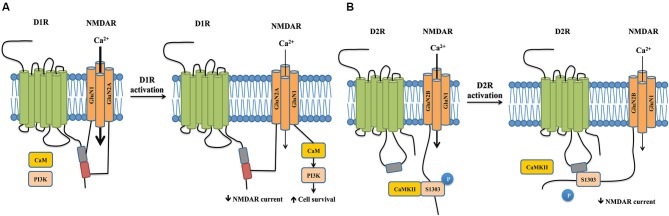
Crosstalks between dopamine and NMDA receptors mediated by physical interactions between the two receptors. (A) Physical interaction between D1R and NMDAR reciprocally regulate receptor properties and trafficking. The carboxyl tails of NMDAR subunits GluN1 and GluN2A individually binds to separate sites on the D1R carboxyl tail. D1R activation inhibits NMDAR currents through the physical interaction between GluN2A and D1R by reducing the surface number of NMDARs, which appears to impact working memory. In contrast, activation of D1R promotes the dissociation of GluN1 and D1R. This allows the recruitment of CaM and PI3K to GluN1, which activate PI3K-dependent cell survival signals and promote cell survival. (B) The carboxyl tail of GluN2B binds to the third intracellular loop of the D2R. Activation of D2R promotes its association with GluN2B, which in turn disrupts the binding between GluN2B and CaMKII. This leads to a decrease in CaMKII activity, resulting in reduced phosphorylation of Serine1303 of GluN2B and hence reduced NMDAR currents.
