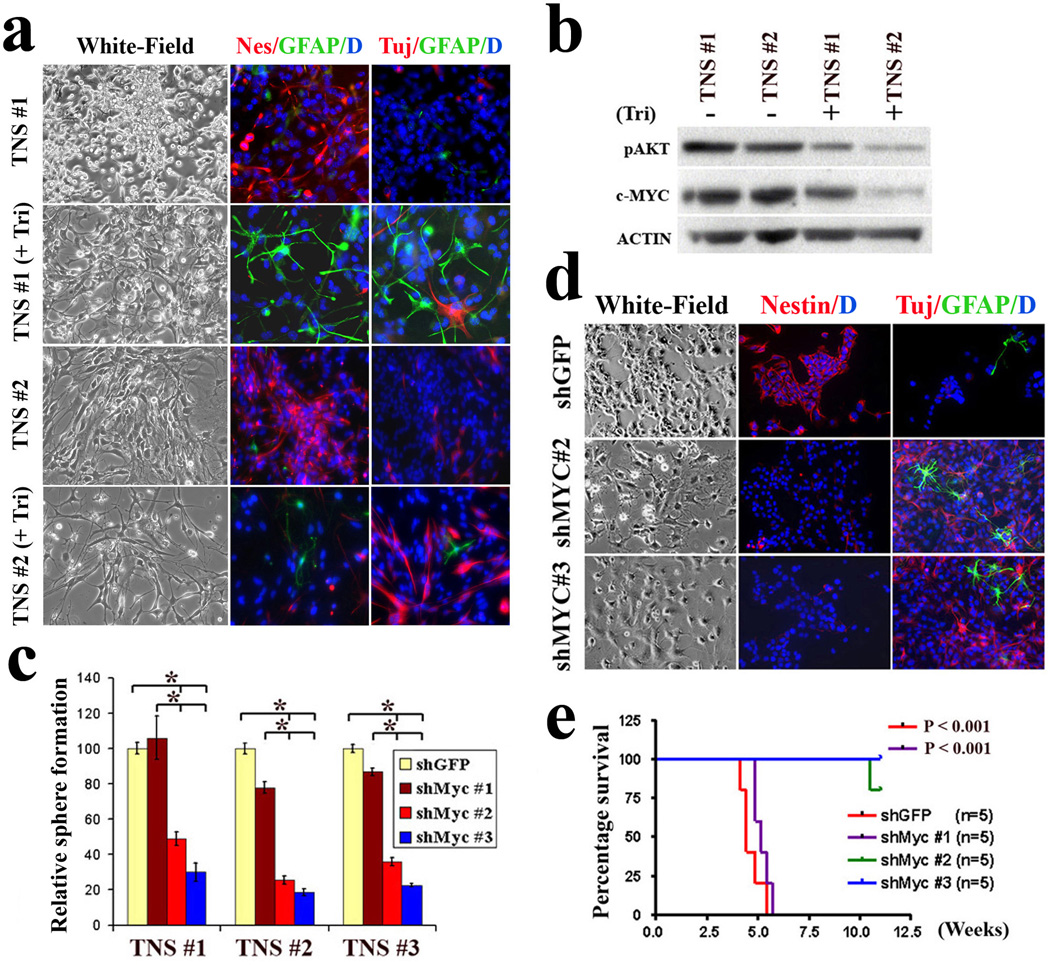
Figure 4. Attenuated c-Myc expression restores hGFAP-Cre;P53lox/lox;Ptenlox/+ TNS differentiation potential and reduces tumorigenic potential.
a, Inhibition of the AKT pathway by triciribine induces TNS cell differentiation. Two independent TNS lines were cultured in 1% FBS in the absence or presence of triciribine (5 µM) for 7 days before being subjected to immuno-staining with antibodies against Nestin (red), GFAP (Green) and Tuj1 (red).
b, Inhibition of the AKT pathway in TNS cells with triciribine attenuates their cellular c-Myc expression.
c, Knockdown of c-Myc expression in TNS cells reduces their self-renewal potential assessed by sphere formation (*P < 0.001, n=3). Values represent mean ± s.d. from three experiments.
d, ShRNA-mediated reduction of c-Myc expression in TNS cells sensitizes cells to differentiation stimuli. Cells infected with control and indicated shRNA were incubated with differentiation medium before subjected to indicated lineage marker analysis.
e, ShRNA-mediated reduction of c-Myc expression represses TNS tumorigenic potency in orthotopically transplanted SCID mice.